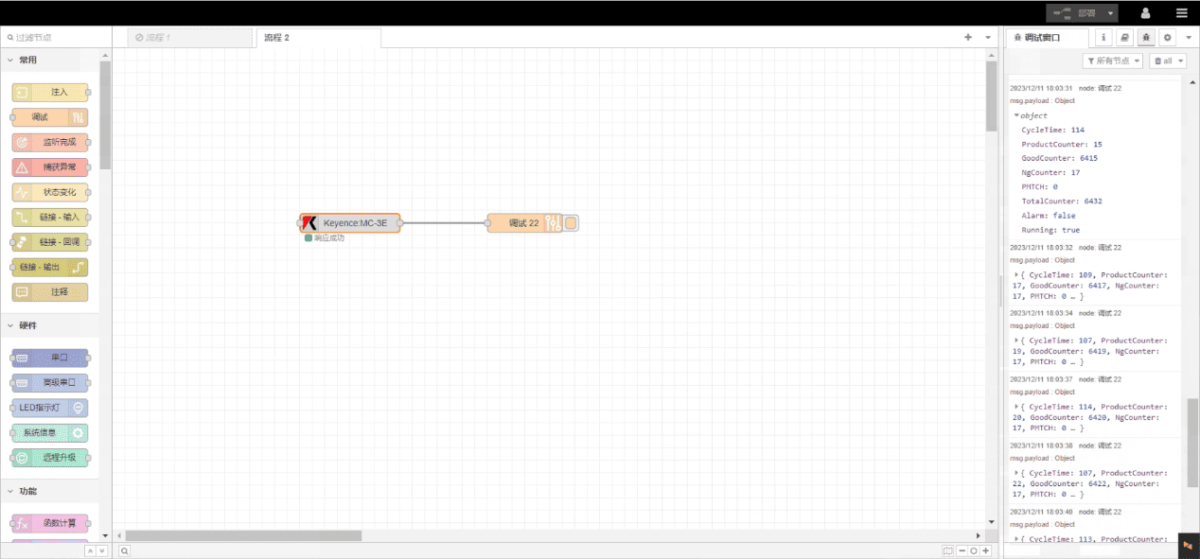
In this tutorial, we will focus on EG series edge computing gateway with PLCs. We hope this proves helpful.
L'articolo di cui abbiamo parlato prima:
Come integrare il gateway di edge computing EG con General Electric PLC
Come integrare il PLC Xinjie tramite il protocollo Modbus RTU
Today, let’s talk about how to interface the EG edge gateway with Keyence KV-8000 series PLCs via the MC-3E protocol.
Compatible PLC: KV-8000 Series
1. Connessione hardware
The MC-3E protocol utilizes Ethernet communication. Therefore, simply ensure the gateway’s LAN port and the Keyence PLC’s IP address are within the same subnet.
| EG8200Mini(LAN) | KV-8000 | |
| Indirizzo IP | 192.168.1.100 | 192.168.1.1 |
2. Parametri di comunicazione del PLC
IP: 192.168.1.1
Porto: 5000
3. Gateway Settings
3.1. Impostazioni di connessione del PLC
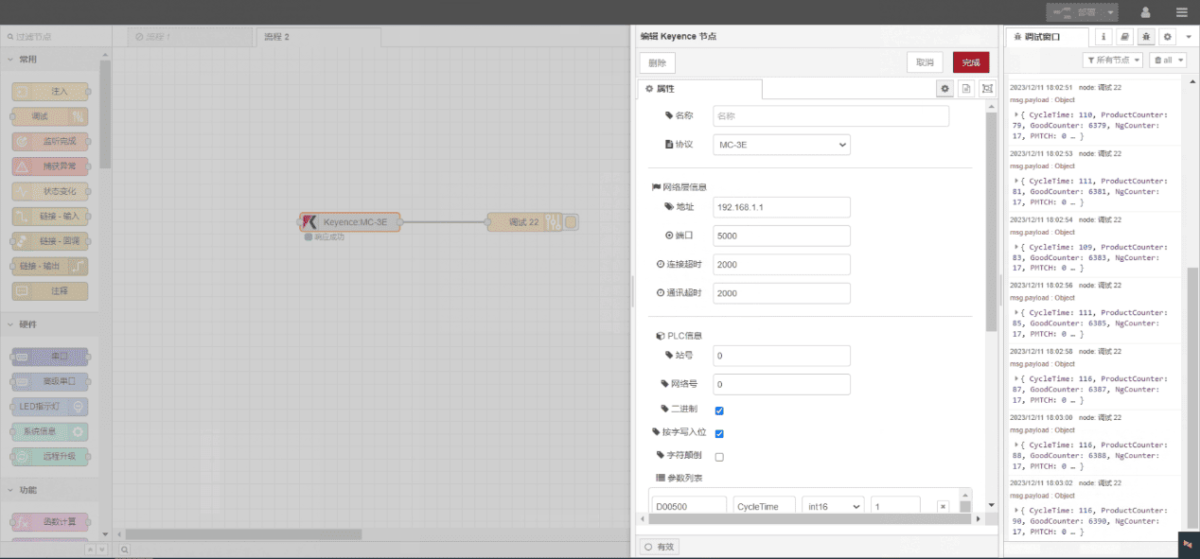
Trascinare un nodo Keyence dal pannello di sinistra, fare doppio clic per aprire la pagina delle impostazioni e configurare come segue in base ai parametri di comunicazione del PLC:
Protocollo: MC-3E
Porta di rete: Collegato alla porta LAN del gateway
Indirizzo: 192.168.1.1
Porto: 5000
Timeout della connessione: 2000
Timeout di comunicazione: 2000
ID stazione: 0
Network ID: 0
Binary: √
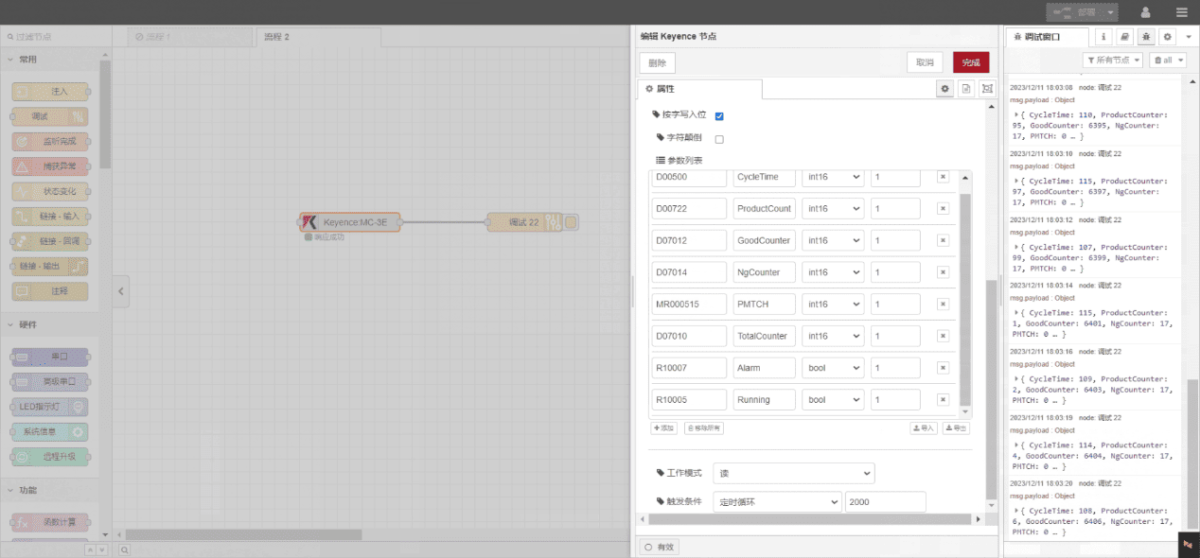
3.2. Configurazione del punto dati
Inserire i punti dati da leggere nell'elenco dei parametri del nodo Keyence. Una volta configurato, il nodo leggerà automaticamente i dati dal PLC alla frequenza specificata.
Data points are typically provided by PLC engineers. Upon receiving the point list, fill in the data points according to the gateway’s required format. For specific correspondence, refer to:
This is a Yueque content card. Click the link to view:(È possibile utilizzare Google Chrome per la traduzione.) https://iotrouter.yuque.com/zn3vdn/eg8000/wgvrbfp0ivzdod3h
This example reads data from multiple addresses such as DM00500 and DM00722. In the parameter list, enter each entry in the following order: Address/Name/Data Type/Data Length. The data is read cyclically every 2 seconds, as shown in the diagram:
3.3. Test
Click Deploy and observe that a data point is printed every 2 seconds. Verify that the returned data point name and corresponding value appear—communication is successful!