Wireless sensor network (WSN) is a collection of small sensor nodes with sensing, computing and transmission capabilities. Since the functions of a single sensor node are limited, especially energy storage and data storage, a good network topology and routing protocol need to be developed. This paper focuses on the Zig Bee wireless sensor network based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard, and proposes an efficient clustering topology MSCT based on the minimum spanning tree (MST). The ultimate goal is to build a network topology with the minimum cost. The topology in this paper also takes indoor environments into account, proposing metrics to handle path loss and signal attenuation caused by walls and obstacles, and calculating the weights of links between nodes. Finally, the MSCT topology proposed in the paper is more advantageous than the Cluster-Tree topology through energy loss and network life.
Each of the three Zigbee network structures has its own advantages. The Zigbee network currently has three architectures: star, tree and mesh. You can choose the appropriate Zigbee network structure according to actual project needs.
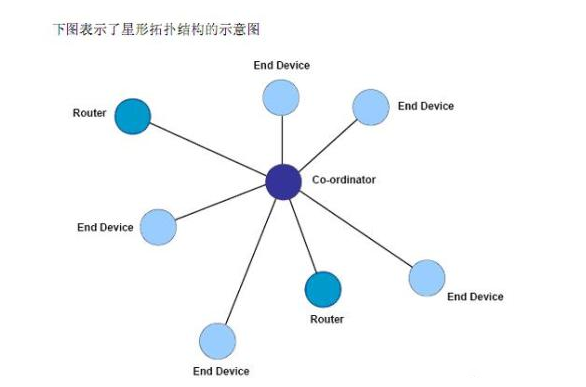
1. Star topology
Es la topología más sencilla. Contiene un nodo coordinador y una serie de nodos de dispositivos finales. Cada nodo de dispositivo final sólo puede comunicarse con el nodo coordinador. Si es necesaria la comunicación entre dos nodos de dispositivo final, la información debe transmitirse a través del nodo coordinador.
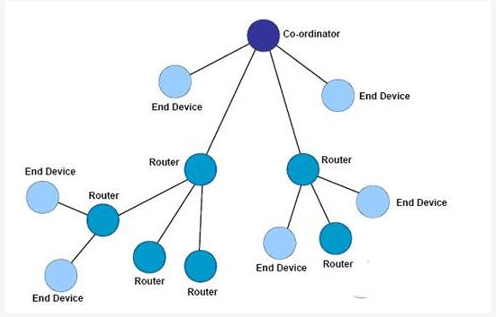
2. Tree topology
La topología de árbol incluye un Coordinador y una serie de nodos Enrutadores y Dispositivos Finales. El coordinador conecta una serie de encaminadores y dispositivos finales, y su subnodo encaminadores también puede conectar una serie de encaminadores y dispositivos finales. Esto puede repetirse en varios niveles. La estructura de la topología de árbol se muestra en la siguiente figura:
hay que tener en cuenta es:
Los nodos Co-ordinator y Router pueden contener sus propios nodos hijos.
El Dispositivo Final no puede tener sus propios nodos hijos.
Los nodos con el mismo nodo padre se denominan nodos hermanos
Los nodos con el mismo nodo abuelo se denominan nodos primos.
Reglas de comunicación en topología de árbol:
Cada nodo sólo puede comunicarse con su nodo padre y sus nodos hijos.
Si hay que enviar datos de un nodo a otro, la información se transmite por la ruta ascendente del árbol hasta el nodo antepasado más cercano y luego por la descendente hasta el nodo de destino.
La desventaja de esta topología es que sólo hay un canal de enrutamiento para la información. Además, el enrutamiento de la información corre a cargo de la capa de pila de protocolos, y todo el proceso de enrutamiento es completamente transparente para la capa de aplicación.
The construction of the network is different from the Cluster-Tree structure described previously. It is based on minimum spanning tree. Assume that the graph G = (V, E) represents the topology of a static sensor network, where V represents a sensor node and E represents the link weight between two connected nodes. Theoretically, the link weight of a sensor network represents the Euclidean distance between two nodes, but as explained in the previous section, path loss and signal attenuation due to obstacles in the indoor environment must be taken into account. The weights are sorted using the “Kruskal” based algorithm [6-7] (Algorithm 1, shown below). According to this algorithm, the topology with the minimum communication transmission cost can be obtained.
3. Topología de malla
La topología de malla incluye un Coordinador y una serie de Enrutadores y Dispositivos Finales. Esta forma de topología de red es igual que la topología de árbol; consulte la topología de red de árbol mencionada anteriormente. Sin embargo, la topología de red en malla tiene reglas de encaminamiento de la información más flexibles, y los nodos de encaminamiento pueden comunicarse directamente entre sí cuando es posible. Este mecanismo de enrutamiento hace que la comunicación de información sea más eficiente, y significa que una vez que se produce un problema en una ruta de enrutamiento, la información puede transmitirse automáticamente a lo largo de otras rutas de enrutamiento. A continuación se muestra un diagrama esquemático de una topología de malla:
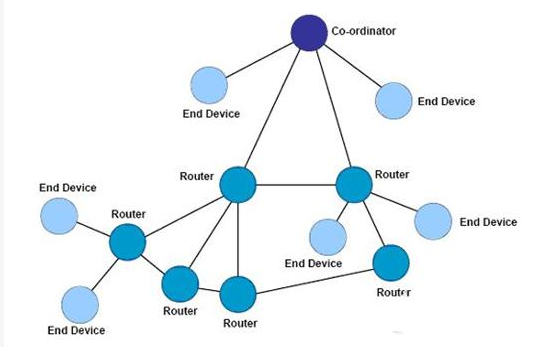
Normalmente, en la implementación de redes malladas de soporte, la capa de red proporcionará la correspondiente función de exploración de rutas. Esta función permite a la capa de red encontrar la ruta óptima para la transmisión de información. Cabe señalar que todas las funciones mencionadas anteriormente son implementadas por la capa de red, y la capa de aplicación no necesita ninguna participación.
The MESH mesh network topology has powerful functions. The network can communicate through “multi-level hops”; this topology can also form an extremely complex network; the network also has self-organizing and self-healing functions;
With the rapid development of wireless sensor networks, wireless technology is widely used in base stations that transmit surveying and mapping data [1]. Wireless sensor networks require large-area deployment in practical applications. Once the deployment is completed, it is relatively difficult to change the deployment again. This is why it is necessary to efficiently use the limited resources of each node in the network. There are many application fields of wireless sensors, such as temperature and humidity monitoring, home automation, rescue monitoring, etc. Most applications require large-scale wireless transmission and need to be supported by standards such as IEEE802.11b. Relevant studies have shown that traditional wireless standards such as Bluetooth and WLAN [2] are no longer suitable for applications in home automation and industrial indoor detection scenarios. The IEEE802.15.4 standard is usually chosen for this application scenario. This paper focuses on the study of the efficient clustering topology MSCT based on the minimum spanning tree (MST) under the condition of indoor wall interference. 1Cluster-Tree network topology Cluster-Tree is a network topology based on the IEEE802.15.4 standard. In wireless sensor networks, energy consumption is an important part that must be considered. This article will first study the efficiency of Cluster-Tree network topology in terms of energy consumption [3]. The Cluster-Tree network topology is divided into two hierarchical relationships, parent and child, as shown in Figure 1. In this topology, each cluster node communicates through the head node of this level, and the head node of each layer is controlled by the PAN coordinator [4]. The topology is constructed through association requests and association responses. In order to achieve the best control effect of the ZigBee network type, the number and extension depth of each parent node’s child nodes must be within a certain range. The depth here refers to the distance between the PAN coordinator and the node. For example: the node of the PAN coordinator is regarded as level 0, and the child node of the PAN coordinator is regarded as level 1
Keywords: data transmission terminal