A step-by-step guide for engineers to know how to quick start the EC ARM Industrial Computer up and running. This guide covers LED indicators, device connection, network setup, remote access, and system configuration.
1. Preparation
1.1 LED Indicators
| Indicator |
Funktion |
Status |
Beschreibung |
| POW |
Strom |
Off |
Power abnormal |
| Auf |
Power normal |
| RUN |
System Status |
Off |
The system program is not running |
| 600ms On / 600ms Off |
Program running but not connected to the Internet |
| 100ms On / 2800ms Off |
Program running and connected to the Internet |
| LED1~LED4 |
User-defined |
Custom |
Customizable |
1.2 Quick Start: Connecting Your Device
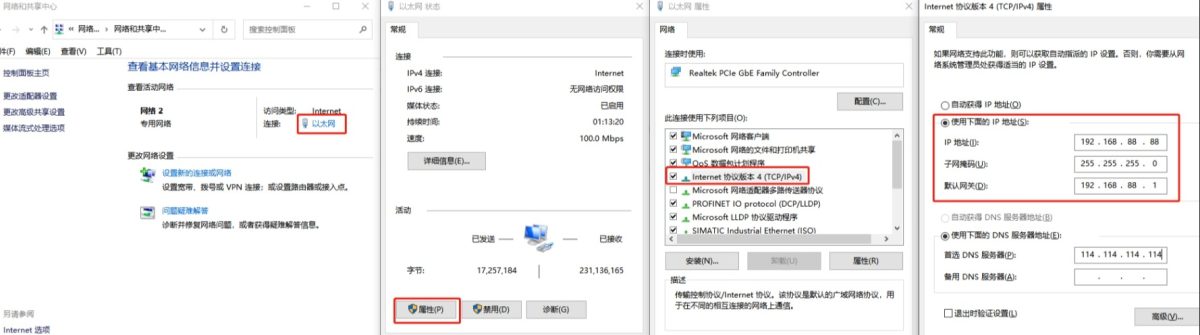
Method 1: Connect your PC to the device’s LAN port using an Ethernet cable.
Since the device’s LAN port has a default IP of 192.168.88.1. You need to set your PC’s IP address to the same subnet (e.g., 192.168.88.x), as shown below:
Method 2: Connect your PC to the device’s hotspot via WiFi.
Once connected, the device will assign your PC an IP address in the 192.168.88.x subnet, as shown:
💡Note: The EC100 series does not have WiFi, so it cannot be connected via WiFi.
2. Instructions for Use
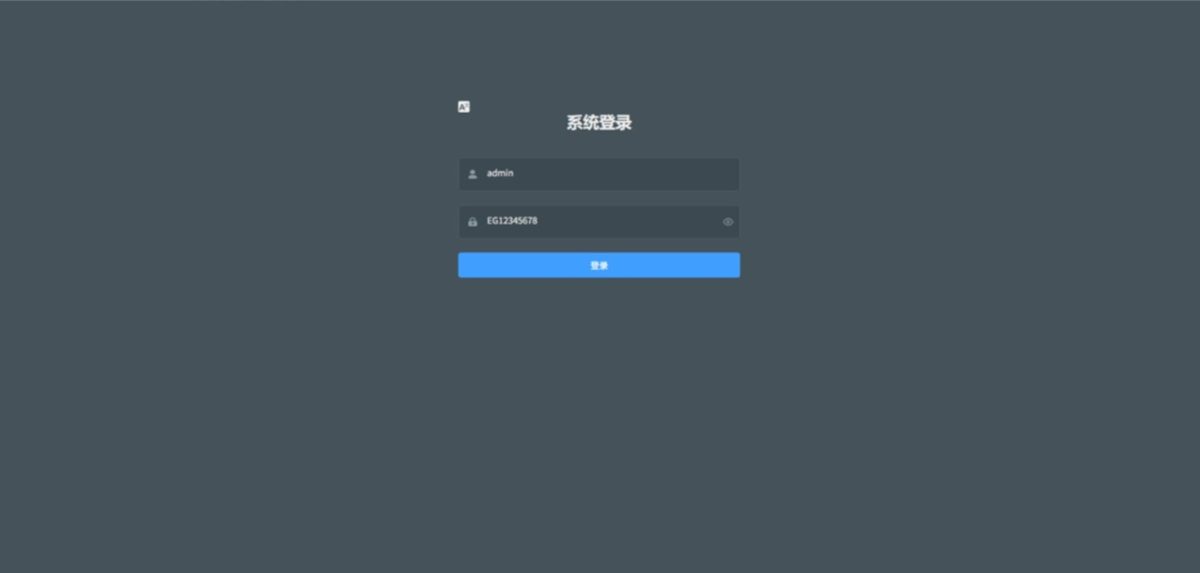
2.1 Login Page
Open a browser and enter 192.168.88.1. In the address bar to access the login page.
Default admin password: EC12345678 (can be changed after login).
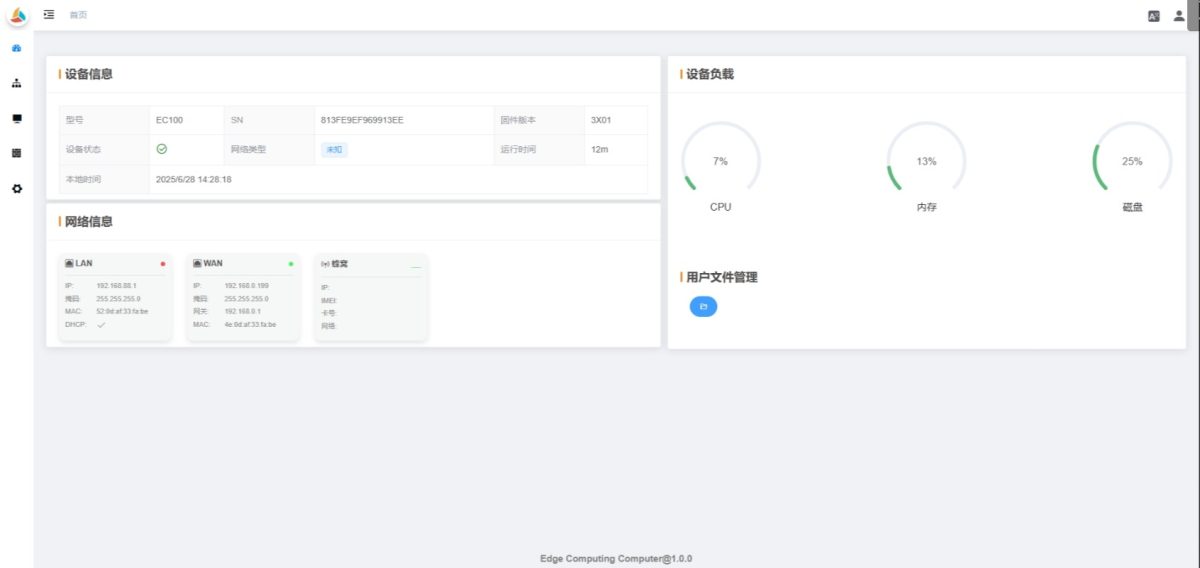
2.2 Dashboard
The dashboard displays the device’s basic information, network status, resource usage, and user file management under the /home directory.
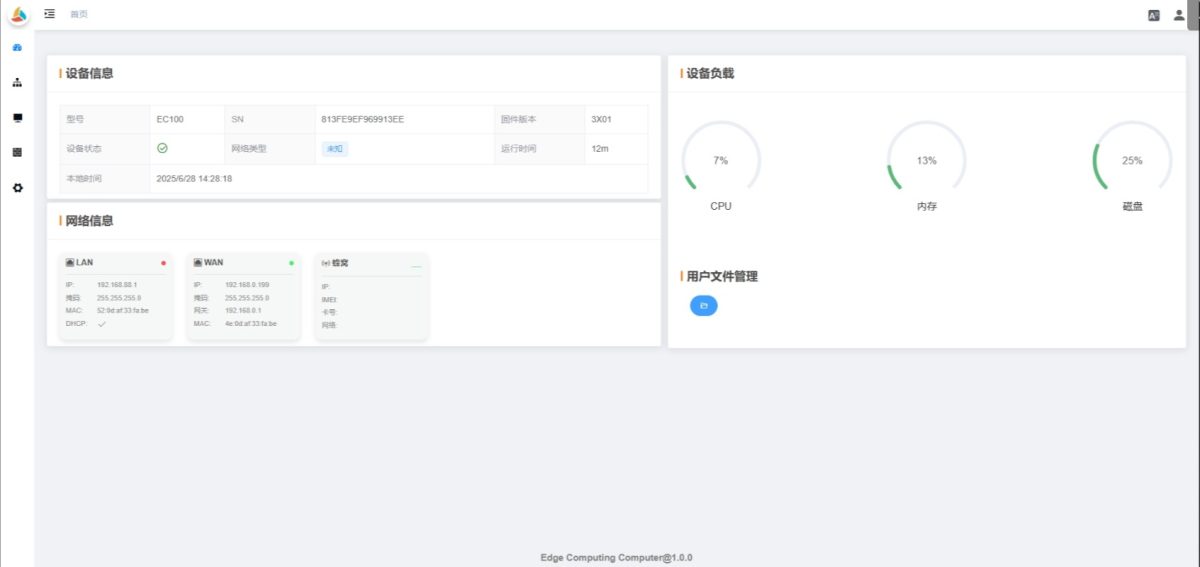
2.2.1 Device Information
-
Model: Displays the specific device model
-
SN: Device serial number, globally unique, usually used as the device identifier
-
Firmware Version: Current firmware version (as shown on the device)
-
Device Status: Current operating status of the device
-
Netzwerk-Typ: Current network connection type (Unknown if not connected)
-
Uptime: Time since the device was powered on
-
Local Time: Current device time
2.2.2 Network Information
LAN Status:
-
Status Icon: Green = connected / Red = disconnected
-
IP: Current LAN IP address
-
Subnet Mask: Current LAN subnet mask
-
MAC: LAN MAC address
-
DHCP: DHCP enabled (√) / disabled (×)
WAN Status:
-
Status Icon: Green = connected / Red = disconnected
-
IP: Current WAN IP address
-
Subnet Mask: Current WAN subnet mask
-
Gateway: Current WAN gateway
-
MAC: WAN MAC address
Cellular (4G/5G) Status:
-
Status Icon: Signal strength indicator
-
IP: Current cellular network IP
-
IMEI: Cellular module IMEI number
-
SIM Number: Current SIM card number
-
Network: Connected network type (e.g., LTE-4G)
WiFi Hotspot Status:
WiFi Station Status:
-
Status Icon: Green = connected / Red = disconnected
-
Enabled: STATION mode enabled (√) / disabled (×)
-
SSID: Currently connected WiFi name
💡 Note: Displayed information may vary depending on the device model and network configuration. Always refer to the actual device interface.
2.2.3 Device Load
- CPU: CPU usage percentage
- Memory: Memory usage percentage
- Disk: Disk usage percentage
2.2.4 User File Management

Displays all files under /home. Supports downloading and is commonly used for log management.
2.3 Network Configuration
Used to configure network-related settings.
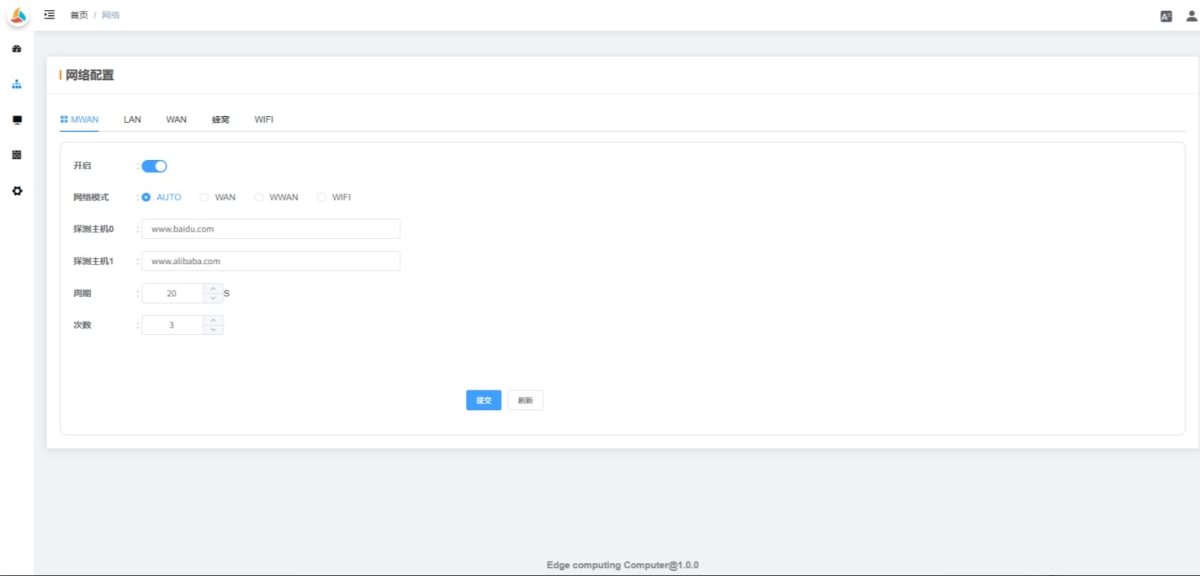
💡 Note: Available options may vary depending on the device model. Always refer to the actual device interface.
2.3.1 MWAN
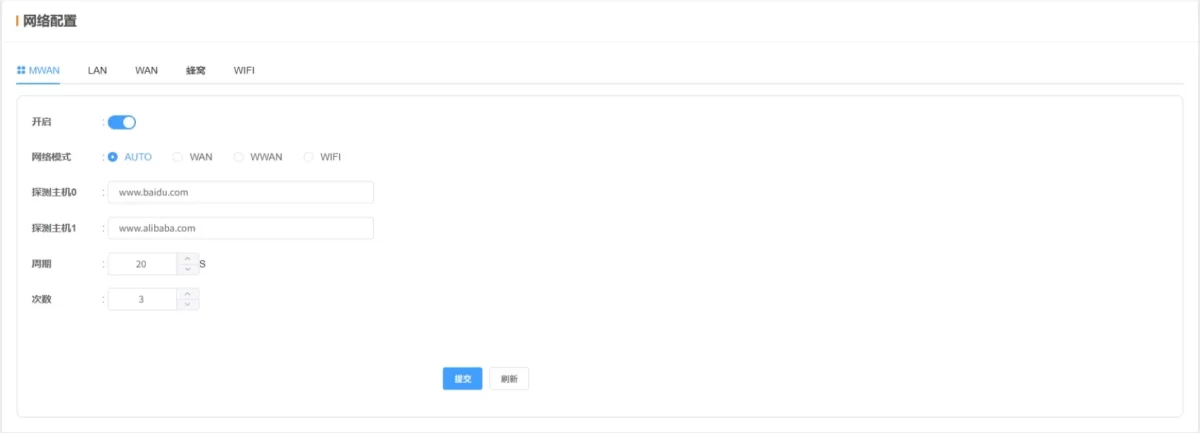
- Enabled: Default ON (do not disable)
- Network Mode: Default
AUTO. Automatically switches the network based on connectivity. If the current network fails, it will try WAN → WiFi → WWAN (4G/5G) sequentially until connected. Other options lock the device to a specific network type.
- Probe Function: Periodically PINGs the configured host to detect network status. In AUTO mode, this triggers automatic network switching. For fixed network mode, probing supports reconnect attempts.
💡 After configuration, click Submit and Reboot to apply changes.
2.3.2 LAN
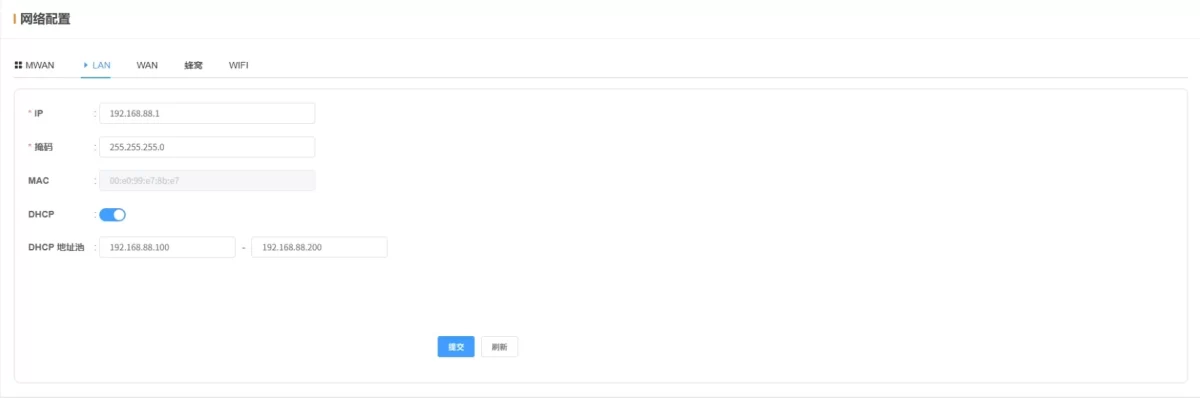
- IP: Default
192.168.88.1 (can be changed after login)
- Subnet Mask: Default
255.255.255.0
- MAC: LAN MAC address
- DHCP Service: DHCP configuration shared for LAN and WiFi
💡 After configuration, click Submit and Reboot to apply changes.
2.3.3 WAN
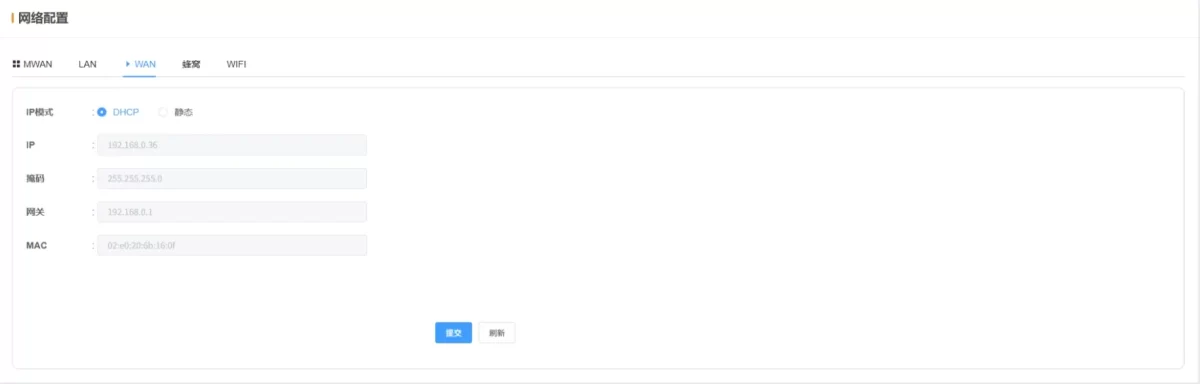
- IP Mode: Default
DHCP
- IP / Mask / Gateway: Auto (DHCP) or manual (Static IP)
- MAC: WAN MAC address
💡 After configuration, click Submit and Reboot to apply changes.
2.3.4 Cellular (4G/5G)
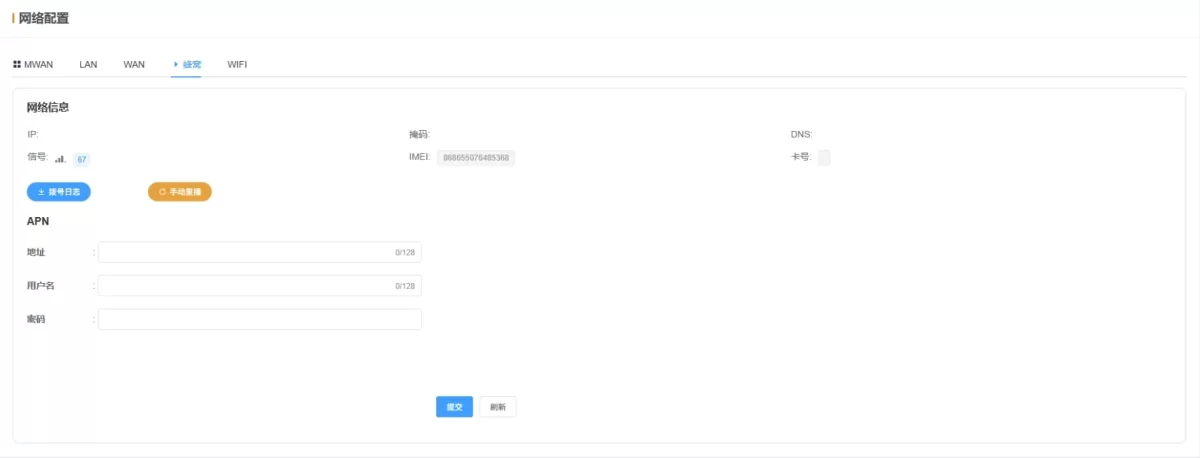
- IP: Current cellular IP address
- Subnet Mask: Current cellular subnet mask
- DNS: Current cellular DNS
- Signal: Cellular signal strength (0–100, higher = stronger; linear mapping to module signal 0–31)
- IMEI: Cellular module IMEI
- SIM Number: SIM card number
- Dial Log: Download recent dial logs for debugging
- Manual Redial: Trigger an immediate redial
- APN: SIM card APN configuration
💡 After configuration, click Submit and Reboot to apply changes.
2.3.5 WiFi
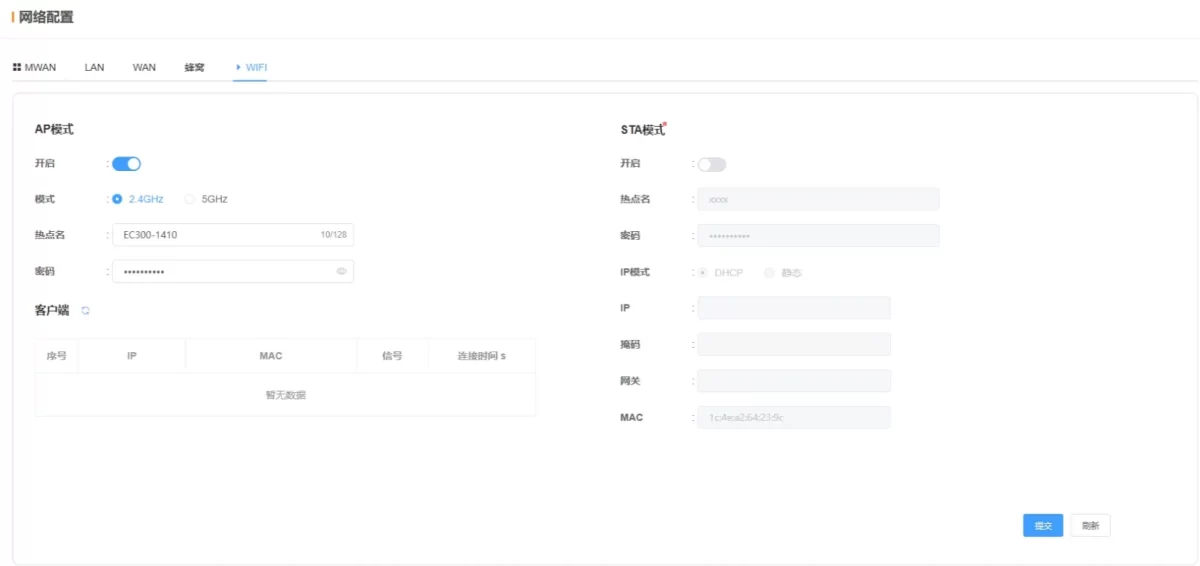
AP Mode:
-
Enabled: Turn on AP mode to provide a hotspot for other WiFi devices
-
SSID: AP hotspot name, default format: DeviceModel-SN last 4 digits (alphanumeric and symbols, max 32 characters)
-
Password: AP hotspot password, default EC12345678
-
Clients: Information about devices connected to the hotspot
STA (Station) Mode:
-
Enabled: Turn on STATION mode to connect to on-site WiFi networks
-
SSID: On-site WiFi name, supports automatic search or manual entry
-
Password: Onsite WiFi password
-
IP Mode: Default DHCP
-
IP / Subnet Mask / Gateway: Auto (DHCP) or manual (Static IP)
-
MAC: STATION mode WiFi MAC address
💡 After configuration, click Submit and Reboot to apply changes.
2.4 Network Setup
Used to configure network-related parameters. For an introduction to the network setup features, please refer to: PLC Remote Maintenance via Ethernet (PC and T100 Ethernet) (to be supplemented later).
💡Once the settings are complete, click Submit to apply.
2.4.1 Basic
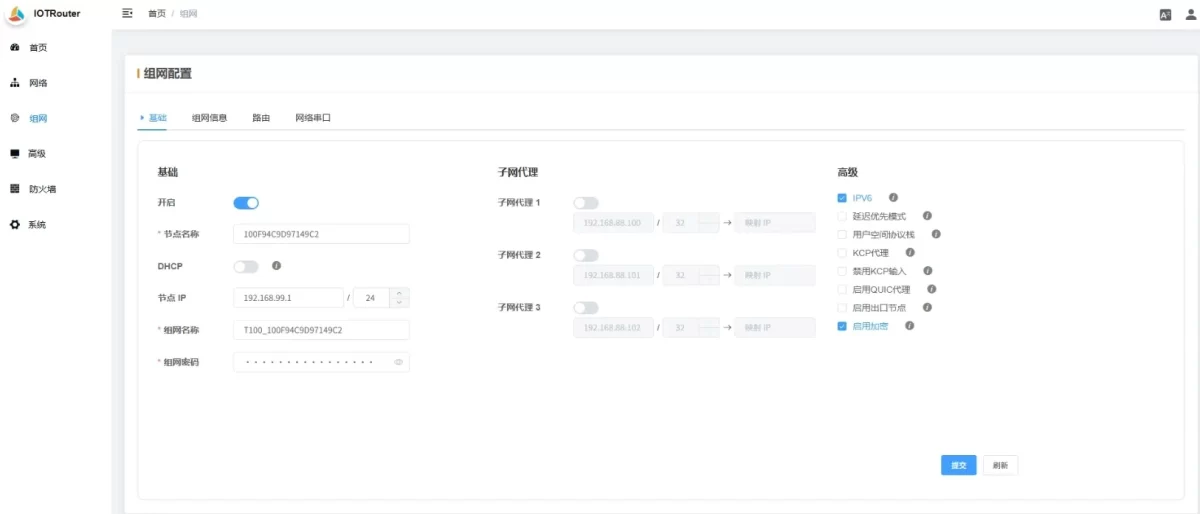
Basic:
-
Enable: Whether to enable the network setup function
-
Node Name: Used to distinguish devices within the network. Ensure that node names are unique within the same network.
-
DHCP: If enabled, virtual IPs are automatically assigned to gateways. It is recommended to set static virtual IPs.
-
Node IP: The gateway’s virtual IP within the network.
-
Network Name: Customizable. Must be the same for all nodes within the same network (length 6–127).
-
Network Password: Customizable. Must be the same for all nodes within the same network (length 6–127).
Subnet Proxy:
Configuration Instructions:
-
Access a Single Device:
To remotely access a device in the local LAN with IP 192.168.0.55:
→ Configure: 192.168.0.55/32 → Mapped IP (leave blank)
-
Access the Entire Subnet:
To remotely access all devices in the local LAN with IP range 192.168.0.X:
→ Configure: 192.168.0.0/24 → Mapped IP (leave blank)
-
Resolve IP Conflicts (Mapping Mode):
If both ends of the network have the same LAN IP range, use IP mapping to avoid conflicts by mapping the target IP to a new range.
→ Configure: 192.168.0.10/32 → Mapped IP: 192.168.1.10
The remote node can then access the device with LAN IP 192.168.0.10/32 via 192.168.1.10.
Advanced:
-
IPv6: Disable IPv6; only IPv4 is used for communication.
-
Latency Priority Mode: Prioritize the path with the lowest total latency, ignoring intermediate hops.
-
User-Space Protocol Stack: Use a user-space TCP/IP stack to avoid OS firewall issues that may block subnet or KCP proxy.
-
KCP Proxy: Converts TCP traffic to KCP to reduce transmission latency and improve speed.
-
Disable KCP Input: Disable inbound KCP traffic; other nodes using KCP will still connect via TCP.
-
Enable QUIC Proxy: Converts TCP traffic to QUIC to reduce latency and improve speed.
-
Enable Exit Node: Allows this node to act as an exit node.
-
Enable Encryption: Must match peer nodes if encryption is disabled.
2.4.2 Network Information
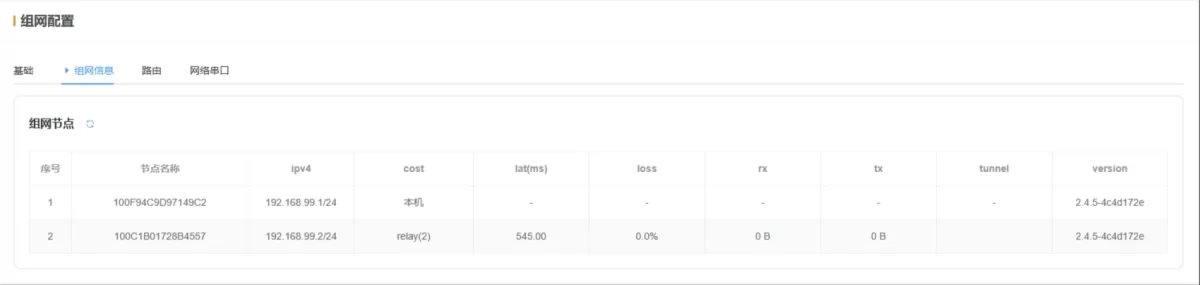
- Network Nodes: Displays node names, node IPs, and other information of devices in the current network.
2.4.3 Routing
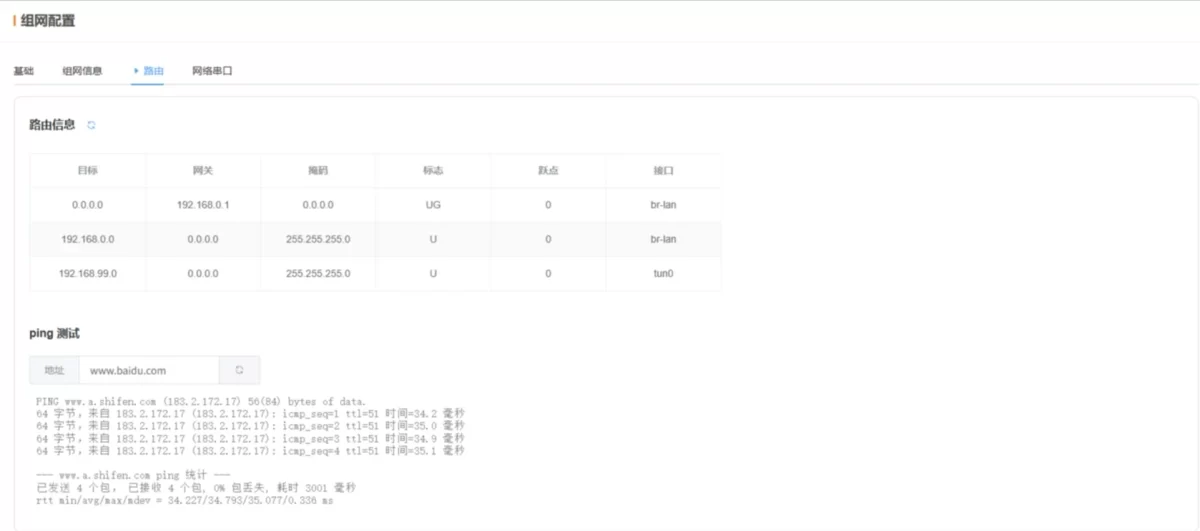
2.5 Advanced
Used to configure advanced parameters.
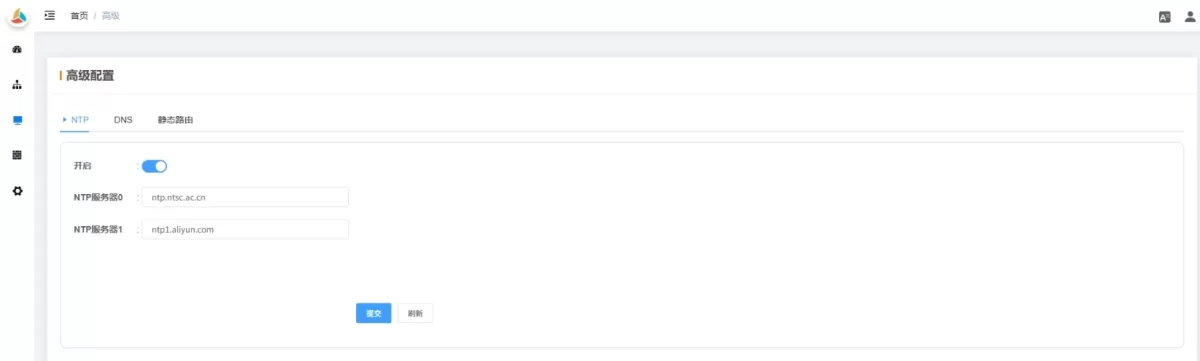
2.5.1 NTP
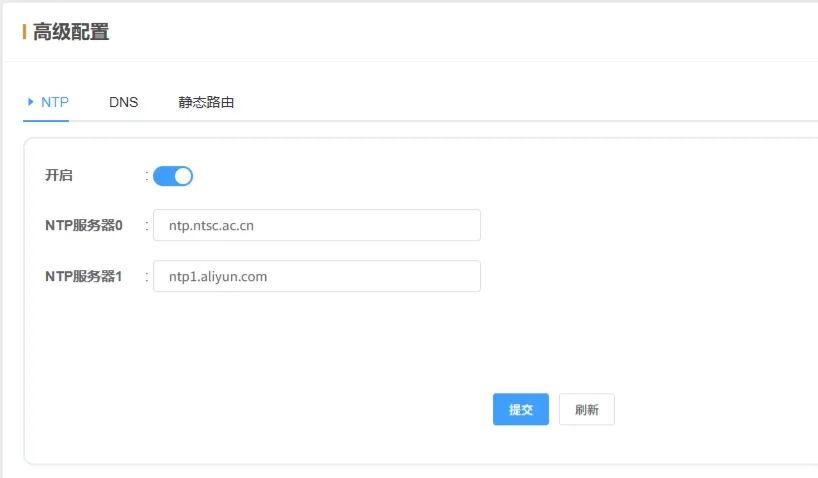
-
Enable: NTP is enabled by default.
-
NTP Server: Address of the NTP server. Modify for private or internal networks if needed.
💡 Once configured, click Submit and restart to apply.
2.5.2 DNS
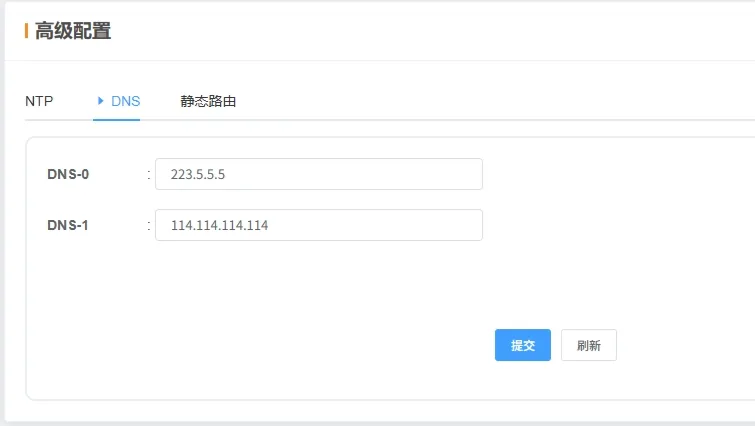
2.5.3 Static Routing
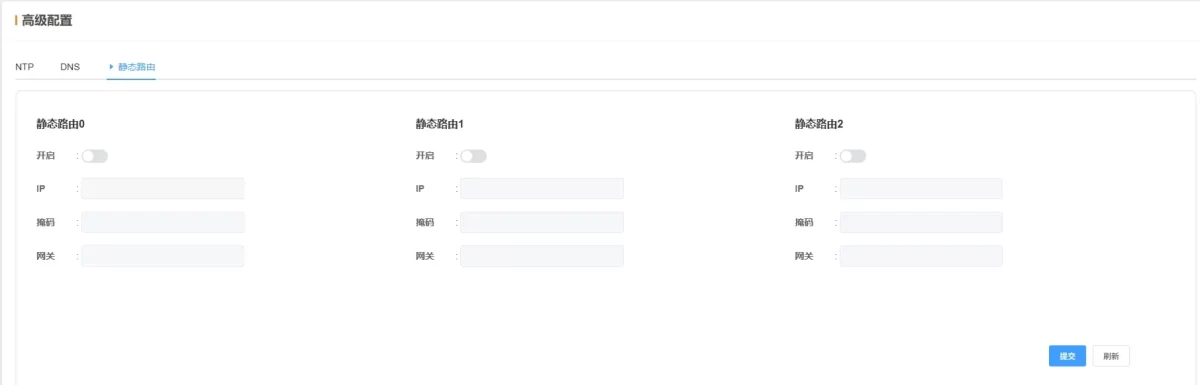
-
Static Routing: Defines exact paths for packets to reach specific networks or hosts, mainly for cross-subnet communication or forwarding via a specified gateway.
-
Enable Status: Supports up to 3 static route rules; disabled by default.
-
IP: Target IP address or subnet.
-
Mask: Use 255.255.255.255 for a single IP, or 255.255.255.0 for a subnet.
-
Gateway: Enter the routing gateway for forwarding packets.
💡 Once configured, click Submit and restart to apply.
2.6 Firewall
Used to configure firewall rules and policies.
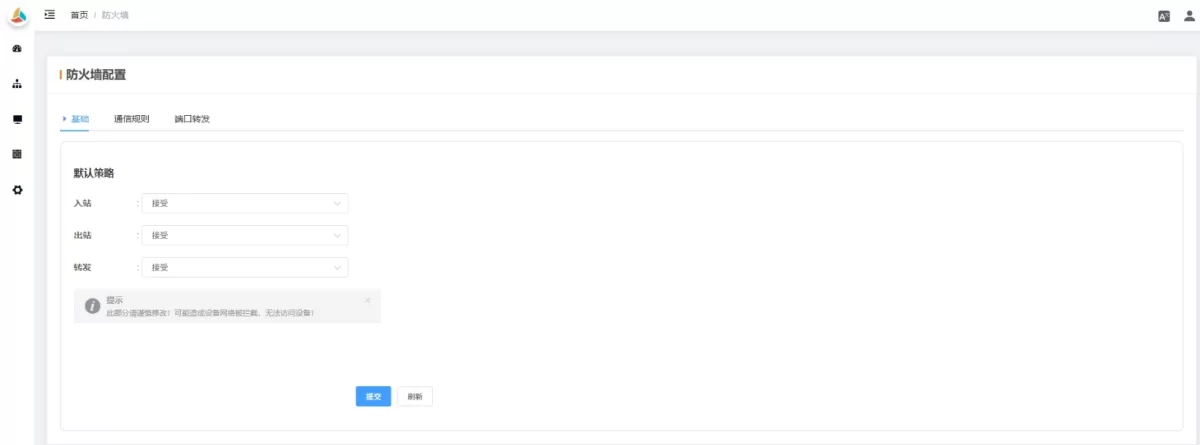
2.6.1 Basic
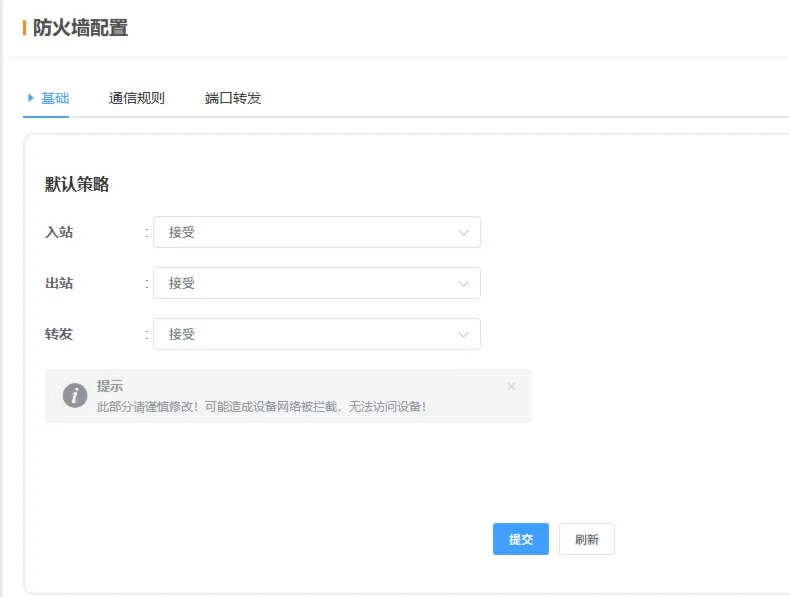
-
Inbound: Default handling of packets from external networks to the device. “Accept” allows all packets not explicitly denied; “Reject” only allows packets matching rules.
-
Outbound: Controls default behavior for packets from the device to external networks. “Accept” allows all outgoing packets; “Reject” blocks all except those explicitly allowed.
-
Forwarding: For devices acting as routers, determines whether packets can be forwarded between networks.
💡 Once configured, click Submit and restart to apply.
2.6.2 Communication Rules
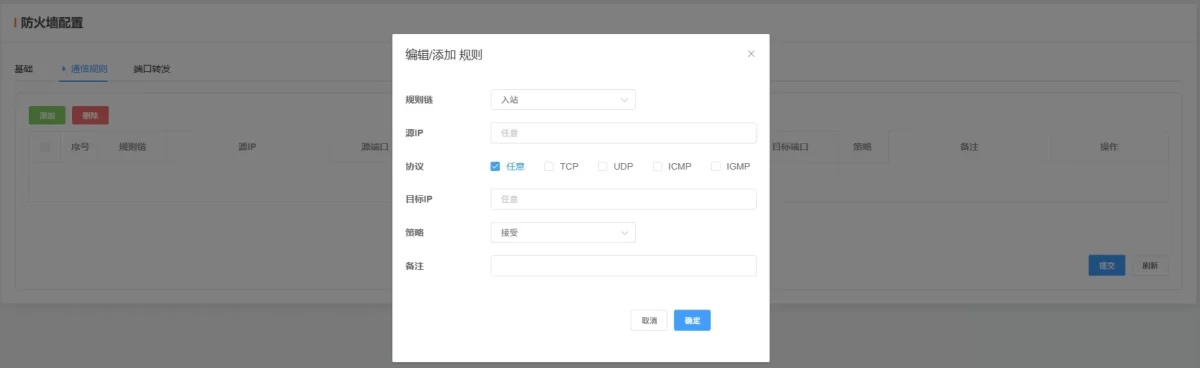
-
Rule Chain: Choose inbound, outbound, or forwarding rules.
-
Source IP: Enter the source IP to allow or block; leave blank to match any IP.
-
Protokoll: Select a protocol; use “Any” to match all protocols if unsure.
-
Destination IP: Enter the target IP; leave blank to match any.
-
Policy: Choose “Accept” (allow) or “Drop” (block).
-
Remarks: Optional note for the rule.
💡 Once configured, click Submit and restart to apply.
2.6.3 Port Forwarding
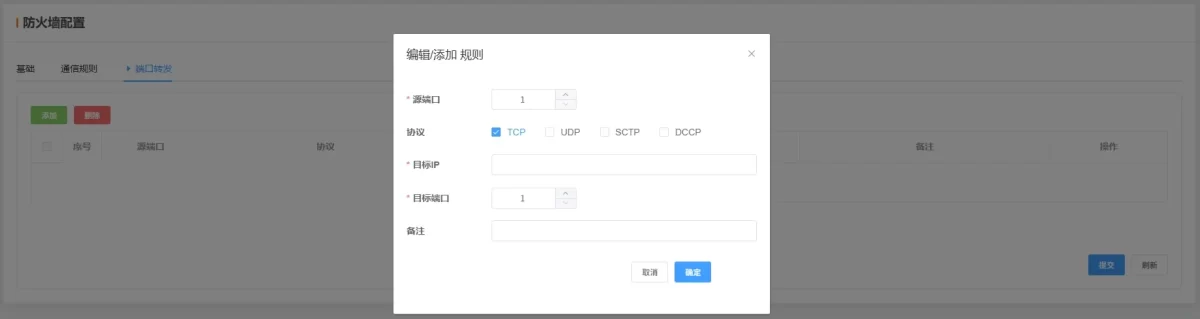
-
Source Port: Enter the source port to forward.
-
Protokoll: Select protocol type (TCP, UDP, SCTP, DCCP). For example, HTTP typically uses TCP.
-
Destination IP: IP of the internal device receiving the forwarded packet.
-
Destination Port: Port on the target device where the application listens.
-
Remarks: Optional note.
💡 Once configured, click Submit and restart to apply.
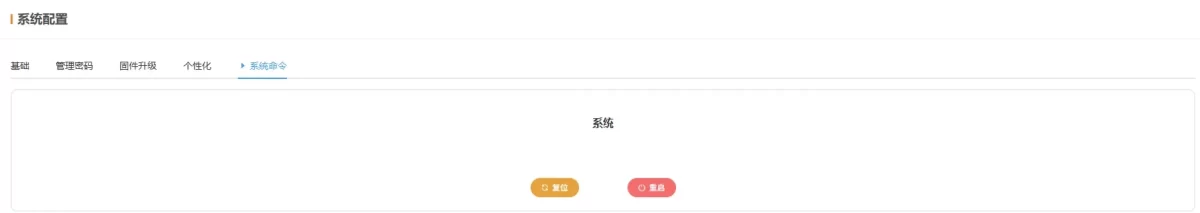
2.7 System
Used to configure system parameters.
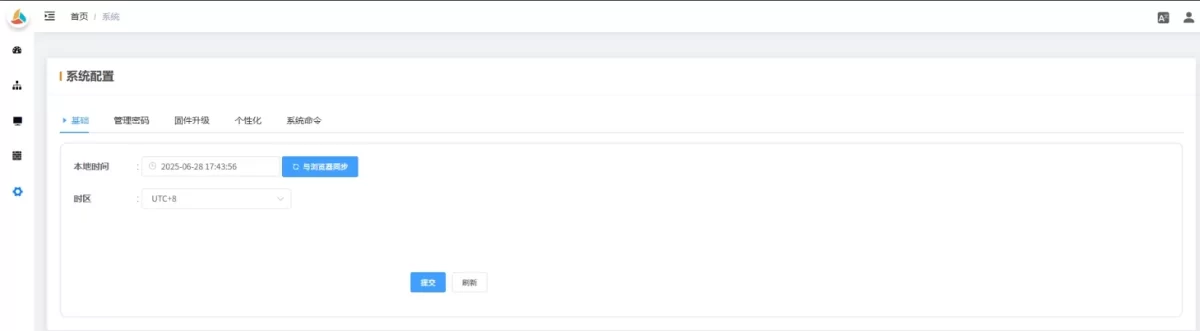
2.7.1 Basic
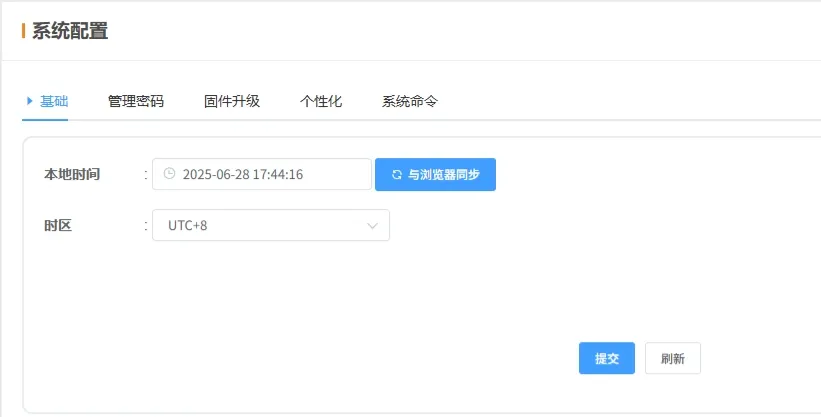
-
Local Time: Device local time. Syncs automatically via NTP. Click Sync with Browser to calibrate immediately.
-
Time Zone: Set the device’s time zone. Correct time zone ensures device time matches local time.
💡 Once configured, click Submit and restart to apply.
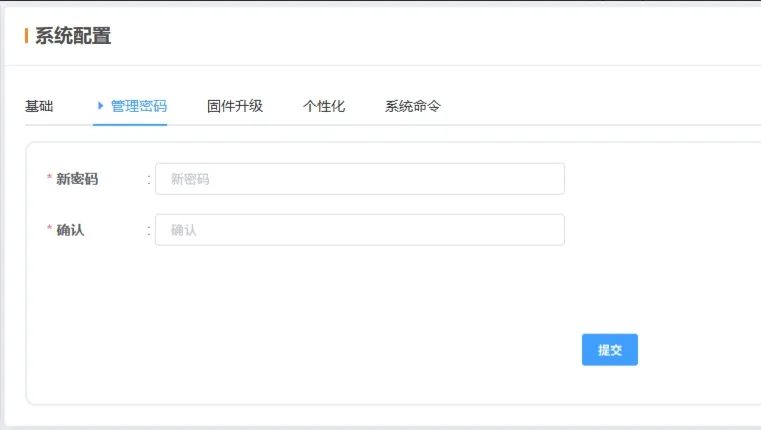
2.7.2 Admin Password
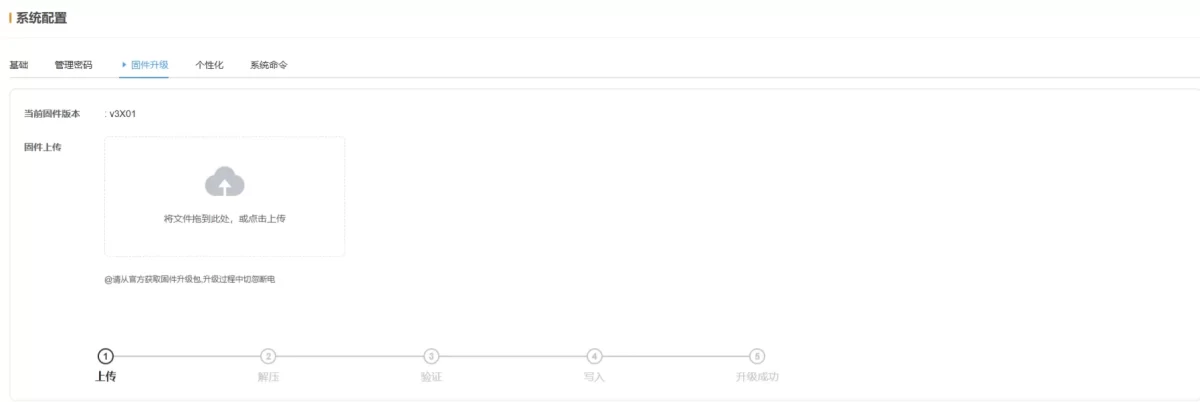
2.7.3 Firmware Upgrade
2.7.4 Personalization
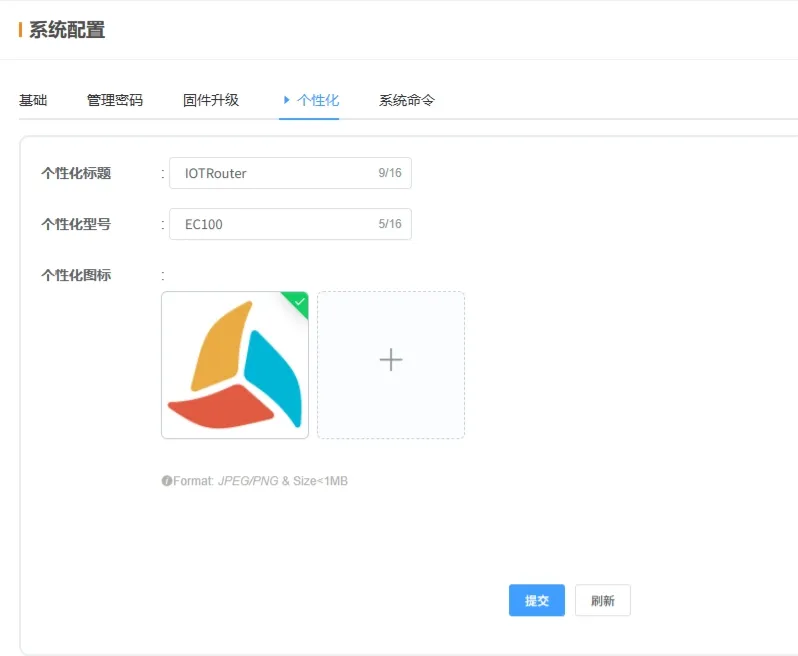
-
Personalization: Customize gateway title, model, and logo (upload icon in the specified format).
💡 Once configured, click Submit and restart to apply.
2.7.5 Service Management
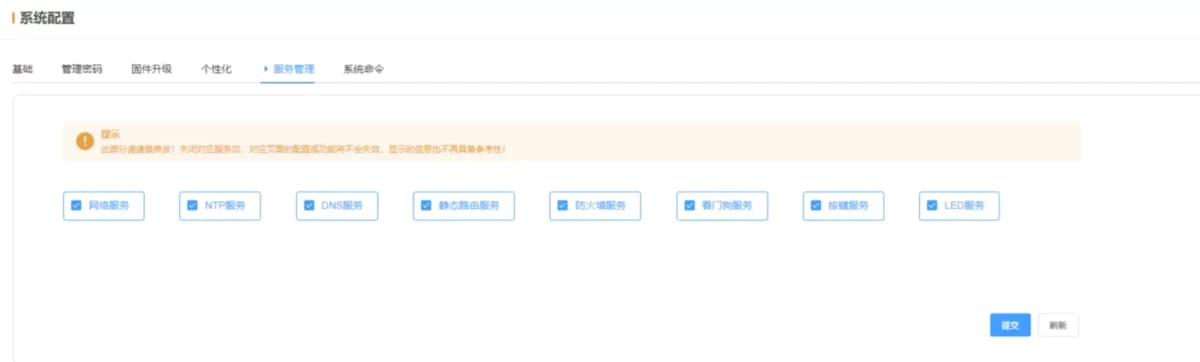
Users can freely enable or disable related sub-services from this page.
2.7.6 System Commands