What’s the difference between Modbus TCP and Modbus RTU? That’s a great question — and one worth exploring. Before diving into the differences, let’s first understand what the Modbus Protocol actually is.
Overview of Modbus Protocols
The Modbus protocol, developed by Modicon, is a messaging structure used to establish master-slave/client-server communication between devices. Among its various options, the most utilized are Modbus RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) e Modbus TCP (Transmission Control Protocol). Understanding the difference between Modbus TCP and Modbus RTU is crucial, as cost and speed are key factors that set them apart.
History and Evolution
Modicon introduced the Modbus protocol in 1979. Initially, Modbus RTU became the most common implementation due to its simplicity and effectiveness in serial communication. However, with the rise of network technologies, Modbus TCP/IP is rapidly gaining popularity and is poised to surpass RTU in various applications. To modernize Modbus for the 21st century, the open Modbus TCP/IP specification was developed in 1999, allowing for broader adoption in Ethernet-based networks.
Key Features of Modbus
Modbus is an open standard widely used in industrial manufacturing environments. It serves as a universal link implemented by numerous vendors in thousands of devices to transfer discrete/analog I/O and register data between control devices. Communication in Modbus always begins from the master node to the slave node, with slave nodes unable to communicate independently until prompted by the master.
Data Types in Modbus
Different data types are utilized within the Modbus protocol, including:
Coils: Starting from 00001, corresponding to on/off binary outputs (e.g., relays).
Input Bits: Starting from 10001, corresponding to binary inputs (read-only).
Input Registers: Starting from 30001, corresponding to analog inputs (read-only).
Holding Registers: Starting from 40001, corresponding to changeable simulation parameters.
These data types facilitate diverse applications in industrial automation and monitoring.
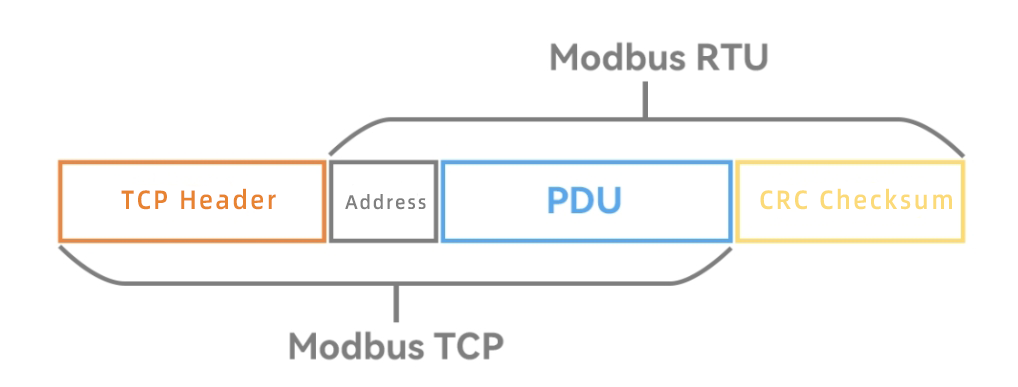
Modbus RTU: Characteristics and Functionality
Modbus RTU is the most common implementation, using binary encoding and CRC error checking. It is an efficient binary protocol where each message is sent in a continuous stream. The format of each byte in RTU mode consists of:
1 start bit
8 data bits (least significant bit sent first)
1 parity bit
1 stop bit
MODBUS RTU packets are exclusively for data transmission and lack the ability to send parameters like point names or units. Standard MODBUS RTU node addresses range from 1 to 254, with 0 reserved for broadcast messages.
Communication Interfaces for Modbus RTU
MODBUS can operate over various physical interfaces, with RS485 being the most common. RS485 configurations typically use a relay cable for direct device connections (daisy chaining). Trunk cable lengths can reach up to 1000 meters, depending on baud rates and network configurations, with a typical baud rate of 9600 bps.
Good cable selection is essential, often using at least 22-gauge wiring to ensure reliable communication. The RS485-MODBUS configuration without repeaters allows devices to be connected directly, but attention must be given to line termination to prevent signal reflections.
Modbus TCP: Advantages and Applications
Modbus TCP/IP is essentially the Modbus RTU protocol adapted to run over Ethernet. This integration combines a universal, scalable network with the TCP/IP standard, facilitating easy data exchange among devices. Modbus TCP/IP is compatible with any existing Ethernet infrastructure, making it simpler to implement in modern industrial settings.

Benefits of Modbus TCP
Ethernet provides faster communication and simplified troubleshooting compared to serial connections. The inherent advantages of Ethernet include:
Higher Data Rates: Ethernet can support significantly higher data rates than serial communication, making it ideal for applications requiring fast data transfer.
Ease of Integration: With widespread Ethernet adoption, integrating Modbus TCP/IP into existing networks is straightforward and cost-effective.
Reduced Wiring Complexity: Using a single Ethernet cable for multiple devices reduces the complexity of wiring compared to traditional serial setups.
However, while Ethernet technology has become a standard for factory networking, speed is not always necessary for many Modbus devices, which often report data every few seconds.
Key Differences Between Modbus TCP and Modbus RTU
The most fundamental difference between Modbus TCP and Modbus RTU is that Modbus TCP operates on the Ethernet physical layer, whereas Modbus RTU functions as a serial protocol. Modbus TCP/IP employs a 6-byte header for routing, simplifying network management compared to the complexities associated with RS485 networks.
In summary, Modbus TCP/IP provides a modern, efficient alternative to Modbus RTU, especially in environments where speed and integration are critical. If your goal is to access data quickly and modernize your system, Modbus TCP/IP is the superior choice. Understanding the difference between Modbus TCP and Modbus RTU will help you make informed decisions about your communication protocols in industrial environments. This ensures that you select the best option for your specific application needs.