With the withdrawal of 2G/3G, the LTE network has become the current mainstream communication network. In addition to NB-IoT, which carries the flag of the medium and low-speed IoT market, Cat.1 may become the main communication standard for cellular IoT, which means that Cat.1 will face a market worth tens of millions or even hundreds of millions.
Cat.1 has advantages in network coverage, speed, and latency. Compared with the traditional LTE Cat.4 module, it has the advantages of low cost and low power consumption. At the same time, Cat.1 adapts to the current 4G network, making it ideal for use in scenarios with high requirements for cost-effectiveness, latency, coverage, and communication speed.

Qual è la differenza tra Cat.1 e Cat.4?
1.Technical level
Cat.1 and Cat.4 are both user terminal category standards for 4G communications LTE networks.Cat is the full name of the LTE UE-Category.Cat.X values are used to measure the wireless performance of user terminal equipment and are primarily used to classify terminal speeds (classes).
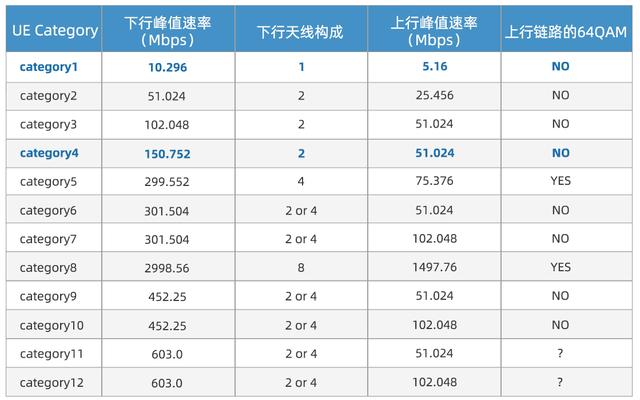
Although Cat.4 can meet the communication needs of mobile broadband, it still cannot meet the communication needs of some IoT devices in some small-sized, battery-powered applications or application scenarios with poor network coverage. Therefore, in order to realize the connectivity of IoT devices, 3GPP has added several enhanced standards to LTE technology, including:
1. LTE Cat.1 with a rate of 10 Mbps, lower power consumption than Cat.4, the same millisecond transmission delay as LTE Cat.4, and support for mobile speeds in excess of 100 km/H. 2.
2. LTE Cat.M2 (NB-IoT) with a rate of only a few hundred Kbps has a strong power advantage, but is not capable of meeting voice and mobility requirements.
2.Application level
Cat.1 is suitable for scenarios that do not have high requirements for broadband speed, but have certain requirements for power consumption and data transmission stability, such as wearable devices, shared payment systems, campus water control, charging piles, smart security systems, smart agriculture applications, and smart home appliances, industrial sensors, and port logistics tracking. These applications often prioritize longevity and reliability over raw speed, making Cat.1 an ideal choice.
For instance, in smart agriculture, remote sensors monitoring soil conditions need to transmit data consistently for extended periods on battery power. Similarly, in port logistics, tracking devices benefit from the stable connection and low power consumption of Cat.1 for reliable asset monitoring. The key here is efficient, consistent data delivery without the need for high bandwidth.
Cat.4 is suitable for scenarios that require higher broadband speed and stability, but are relatively insensitive to cost and power consumption, such as live broadcast media, Internet of Vehicles (IoV), smart grids, video security systems, commercial display equipment, and more. These applications demand real-time or near real-time data transmission and benefit greatly from the increased bandwidth offered by Cat.4.
Consider the Internet of Vehicles, where vehicles need to exchange data rapidly for navigation, safety alerts, and infotainment. Similarly, smart grids require fast, reliable communication for monitoring and controlling power distribution, making Cat.4 a more appropriate solution despite its higher power consumption and cost. Ultimately, the need for speed and responsiveness outweighs concerns about power and price in these applications.
3.Cost
1. In terms of network construction, Cat.1 can be seamlessly integrated into the existing LTE network, without the need for software and hardware upgrades for base stations, and the network coverage cost is low.
2. In terms of chip cost, after system optimization, the module’s hardware architecture is simpler, the integration level is higher, and the peripheral hardware cost is lower.
3. Per quanto riguarda i moduli, il mercato è caratterizzato da numerosi operatori e da un'agguerrita concorrenza, e il prezzo dei moduli Cat.1 è stato continuamente abbassato.
Il Internet of Things has a wide range of application scenarios and complex usage environments. Users should choose the most suitable product based on their actual needs and site conditions. Things like public network intercoms, toy robots, shared bicycles, mobile POS machines, scan-code payment, etc. that require voice support, good mobility, or certain requirements for uplink and downlink speeds/immediacy of data processing, but do not have high mobile broadband communication requirements. scenario, original Cat.4 users can switch to Cat.1.