The Internet of Things technology has made an all-out effort in the prevention and control of the epidemic in 2020, and has become a core element in the new infrastructure. The connection of “things” will give people new data cognition, which will lead to unprecedented changes. A new round of scientific and technological development represented by Internet of Things technology, artificial intelligence, and big data has reached the starting point of a new cycle, from the connection between people to the connection between things, from material production factors to data elements, and from reality The world has become a digital twin, the digital world has fully arrived, and the Internet of Things revolution is ready to take off.
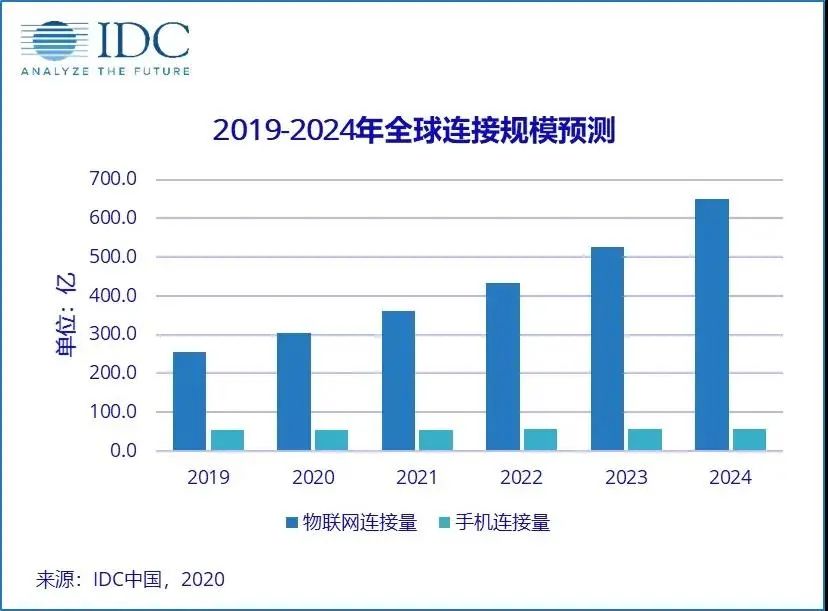
According to relevant reports, 5G will account for less than 1% of IoT connections in 2020, but will rise to 40% of all connections by 2030. The deployment of 5G is accelerating, and with the widespread application of low-power wide area networks such as LoRa and NB-IoT, the number of global IoT connections has surged. From smart cars and smart homes to enterprise asset management equipment and industrial equipment, extensive connections have promoted the transformation of information technology. Mobile Internet moves towards the Internet of Everything. According to the latest report from research firm IDC, the number of global IoT connections will reach 30 billion in 2020, and the number of global IoT connections will be close to 65 billion by 2024. At the 2020 World Internet of Things Conference, Shi Dinghuan, chairman of the organizing committee and former secretary-general of the Ministry of Science and Technology, gave a keynote report in which he estimated the current global output value of the Internet of Things at US$15 trillion, with an average annual growth rate of nearly 23%. He predicted that by 2021 In the future, this growth rate is expected to reach 30%, and by 2025, the global IoT output value will reach 30 trillion US dollars.
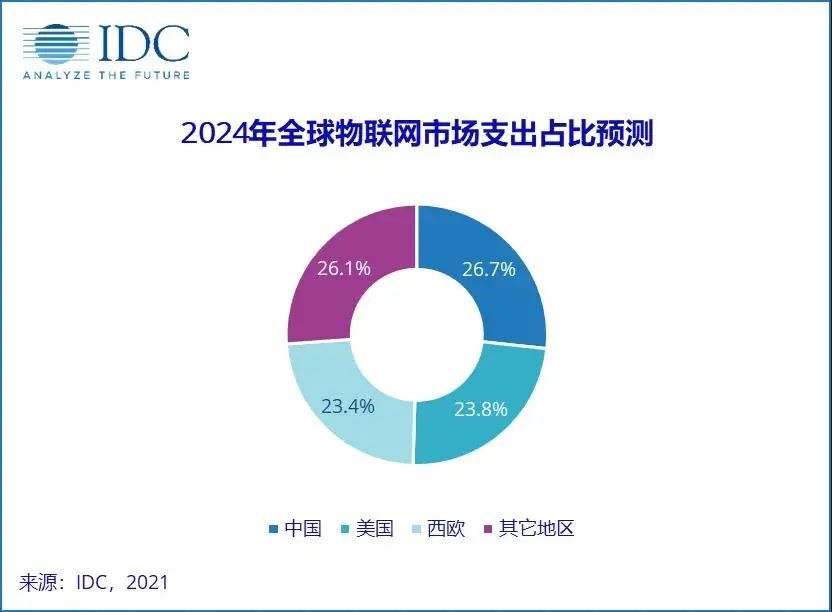
At the same time, thanks to the promotion of artificial intelligence and the drive of global digital and intelligent innovation, spending on the Internet of Things has grown steadily in all sectors. It is worth mentioning that my country is the world’s largest market for IoT spending. The latest report from IDC predicts that my country’s IoT market spending will reach approximately US$300 billion by 2024, with a compound growth rate of 13% in the next five years. This spending surpassing the United States to become the world’s largest IoT market.
The widespread application of the Internet of Things has injected continuous vitality into the Internet of Things industry to flourish. As early as 2018, the scale of my country’s Internet of Things industry exceeded the trillion mark. As the world’s most innovative, dynamic and largest market, my country has strong demand for new technologies such as the Internet of Things and has become an important global Internet of Things market. .
The application of IoT technology has penetrated widely into all walks of life and people’s lives. It is not only testing the endurance of traditional systems, but will also determine the fate of companies large and small in different industries. We look forward to a clearer and more transparent future blueprint for the Internet of Things. The following IoT technology components will provide readers with a map of intelligent and ubiquitous IoT life technology.
MCU
MCU (microcontroller unit) is the core of the Internet of Things. Without the development of MCU, the success of the Internet of Things may not be possible today. In various tasks, MCU is often the central processing element of various interconnected devices. Today, a large number of microcontrollers have entered three areas of IoT applications – smart homes and cities, smart industry, and smart everything. Each application has processing and security requirements. Today’s MCUs are all system-on-chip (SoC), integrating a variety of functional modules and interfaces on a single chip, including memory, I/O ports, clocks, A/D conversion, PWM, etc., as well as SPI, I2C, ISP, etc. Data transmission interface. Divided according to the number of bits, MCUs can be divided into 4-bit, 8-bit, 16-bit, 32-bit and 64-bit. Now 32-bit MCU has become the mainstream. In the applications and markets dominated by 8/16-bit MCU in the past, 32-bit The MCU has basically completed its replacement.
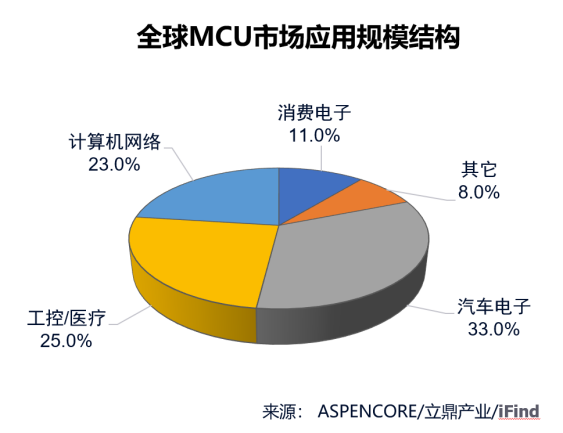
Driven by the Internet of Things, the huge demand for various battery-powered devices has led to increasing industry requirements for energy efficiency in microcontrollers and other system-level devices. Therefore, reducing power consumption has become an unavoidable technical topic. Many manufacturers have begun to compete on the low-power MCU track, and developers are constantly making trade-offs between power consumption and performance.
Connectivity and communication technology
If the highways, railways, and rail transit included in the “rail-road infrastructure” are regarded as networks between sites, then 5G, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, LPWAN, etc. are channels for connecting IoT devices and transmitting data to each other. Statistics from the Global System for Mobile Communications Association (GSMA) show that the global IoT device market grew rapidly from 2010 to 2020, with a compound growth rate of 19%. In 2020, the number of global IoT device connections will reach 12.6 billion. According to GSMA predictions, the number of global IoT devices (including cellular and non-cellular) connected to the Internet will reach approximately 24.6 billion in 2025. In communication technology, Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT), Long Term Evolution Machine Type Connection (LTE-M and LTE-MTC) and Enhanced Machine Type Communications (eMTC) are currently popular technologies. The advantage of these technologies is that they leverage existing cell towers used for voice and high-bandwidth communications. However, devices that only require occasional reporting and control do not require high bandwidth, and since many devices are battery powered, these technology standards are required to support lower power consumption and lower bandwidth standards. Other technologies that do not leverage existing cellular networks and must rebuild infrastructure include Sigfox, LoRa/LoRaWAN, and others.
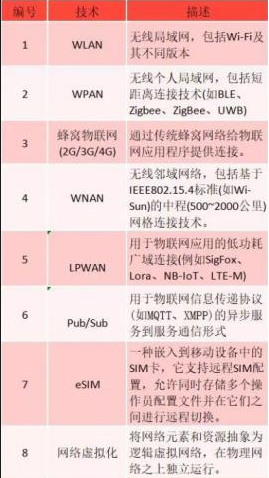
The application of wide area networks and short-range communication technologies is also driving more sensor devices to connect tens of billions of objects into the digital world. The Internet of Things will rely on the next generation of more advanced connection technologies: on the one hand, the cost, power consumption and size of IoT connections will be greatly reduced, enabling low-cost IoT applications through sensorless deployment; on the other hand, the connections provided by the IoT infrastructure Not only is it an information medium, it will also have intelligent end-side signal processing and compression capabilities, thereby building a nerve center that connects the physical world and the digital world, ushering in an era in which all things are perceived, all things are interconnected, and all things are intelligent. In the future, IoT infrastructure will provide ubiquitous signal coverage, provide environmentally friendly and disposable low-cost terminals, and provide smart data collection and analysis services that are more accessible and truly connect everything.
sensor
The Internet of Things has entered people’s lives, and it is inseparable from small sensors. Nowadays, whether it is the forefront of intelligence – smart manufacturing, smart cities, smart medical care, etc., or smart devices and big data analysis, no matter how huge the smart system is, it all starts with sensor sensing. Sensors are composed of sensing elements, signal conditioning circuits, controllers (or processors), and have data collection, conversion, analysis and even decision-making functions. In electronic and electrical equipment, sensors are used to obtain original physical signals from the outside world, including sound, images, temperature, humidity, pressure and light signals, etc., and convert these physical signals into electrical signals, typically in the form of voltage and current. The development of sensors has entered a stage of improving accuracy, reducing power consumption and volume, and enabling easier networking to expand the scope of sensor applications. Traditional physical and chemical sensors only obtain external signals and do not have computing and processing capabilities. As manufacturing process technology, size and cost requirements increase, sensors based on microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) processes are becoming increasingly popular.
Today, the development trends of sensing technology mainly focus on: integration, miniaturization and low power consumption. In terms of integration, in addition to horizontal multi-sensor integration, more and more sensor companies are beginning to do vertical integration: to achieve the construction of a complete system, and may even expand to use software for more complete data processing, and even cloud and AI technologies .
The emergence of low-power smart sensors, innovative connectivity technologies, and amazing use cases is making the Internet of Things hot. In the future, more wireless devices will be connected to the network, and the skyrocketing number of IoT devices will present both opportunities and challenges. Successful IoT solutions require the industry to provide both innovative sensor and connection technologies.