The concept of smart agriculture
“Smart agriculture” evolved from terms such as computer agriculture, precision agriculture (precision agriculture), digital agriculture, and intelligent agriculture. Its technical system mainly includes three aspects: agricultural Internet of Things, agricultural big data, and agricultural cloud platform. “Smart agriculture” is the use of modern high-tech Internet means to combine agriculture with science and technology, and fully modernize the operation mode to change the traditional farming methods.

What is smart agriculture?
Smart agriculture is the smart economy in agriculture, or the specific manifestation of smart economic form in agriculture. For developing countries, smart agriculture is a major component of the smart economy and the main way for developing countries to eliminate poverty, achieve latecomer advantages, catch up with latecomers in economic development, and achieve catch-up strategies.
Smart agricultural greenhouse
Smart agricultural greenhouses are one of the applications of Internet of Things technology in the field of modern agriculture. They mainly include automatic monitoring functions, automatic control functions, real-time image and video monitoring functions.
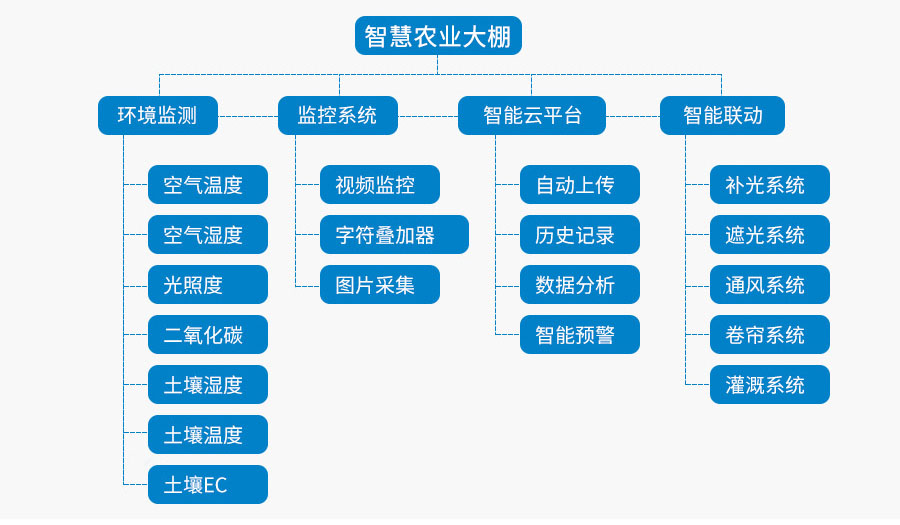
1. Automatic monitoring function
Automatic information detection is realized in the agricultural park by equipping wireless sensor nodes, solar power supply systems, information collection and information routing equipment with wireless sensor transmission systems. Each base point is equipped with a wireless sensor node, and each wireless sensor node can monitor parameters such as soil moisture, soil temperature, air temperature, air humidity, light intensity, and plant nutrient content. Provide various sound and light alarm information and SMS alarm information according to the needs of planting crops.
2. Automatic control function
Obtain plant growth environment information based on the wireless network, such as monitoring soil moisture, soil temperature, air temperature, air humidity, light intensity, plant nutrient content and other parameters. Other parameters can also be selected, such as pH value in the soil, conductivity, etc.
The monitoring function system is responsible for receiving, storing, displaying and managing data from wireless sensor aggregation nodes, achieving the acquisition, management, dynamic display and analysis of all base test point information and displaying it to users in the form of intuitive charts and curves. Based on the feedback of the above various types of information, the system performs automatic control on the agricultural park such as automatic irrigation, automatic cooling, automatic mold rolling, automatic liquid fertilizer fertilization, and automatic spraying.
3. Real-time image and video monitoring function
The basic concept of the agricultural Internet of Things is to realize the relationship network between crops and the environment, soil and fertility in agriculture, and to realize the optimal growth environment conditioning and fertilization management of crops through multi-dimensional information and multi-level processing.
However, as a person who manages agricultural production, the mere numerical connection of things cannot fully create optimal growth conditions for crops. Video and image monitoring provide a more intuitive way of expressing the relationship between things.
More applications of smart agriculture
Compared with traditional agricultural production, smart agriculture does not require planting of vegetables in the soil or even natural light, but the yield can reach 3-5 times that of conventional planting. Irrigation and fertilization do not require manual labor, but are accurately completed by an integrated water and fertilizer irrigation system, which is more efficient than flood irrigation in large fields. 70%-80% water; planting space is not limited to flat surfaces, but can also be vertical and three-dimensional, saving up to 80% of land; there are drones for pesticide application, robots for greenhouse picking, and the entire process of plowing, harvesting, drying grain, and rice processing is mechanized.
Keywords: GPS positioning RTU