Neste tutorial, vamos centrar-nos na gateway de computação periférica da série EG com PLCs. Esperamos que este tutorial seja útil.
O artigo que discutimos anteriormente:
Como integrar a gateway de computação periférica EG com a General Electric PLC
Como fazer a integração com o PLC Xinjie através do protocolo Modbus RTU
Today, let’s talk about how to interface the EG edge gateway with Keyence KV-8000 series PLCs via the MC-3E protocol.
Compatible PLC: KV-8000 Series
1. Ligação do hardware
The MC-3E protocol utilizes Ethernet communication. Therefore, simply ensure the gateway’s LAN port and the Keyence PLC’s IP address are within the same subnet.
| EG8200Mini(LAN) | KV-8000 | |
| IP address | 192.168.1.100 | 192.168.1.1 |
2. Parâmetros de comunicação do PLC
IP: 192.168.1.1
Porto: 5000
3. Definições da porta de entrada
3.1. Definições de ligação do PLC
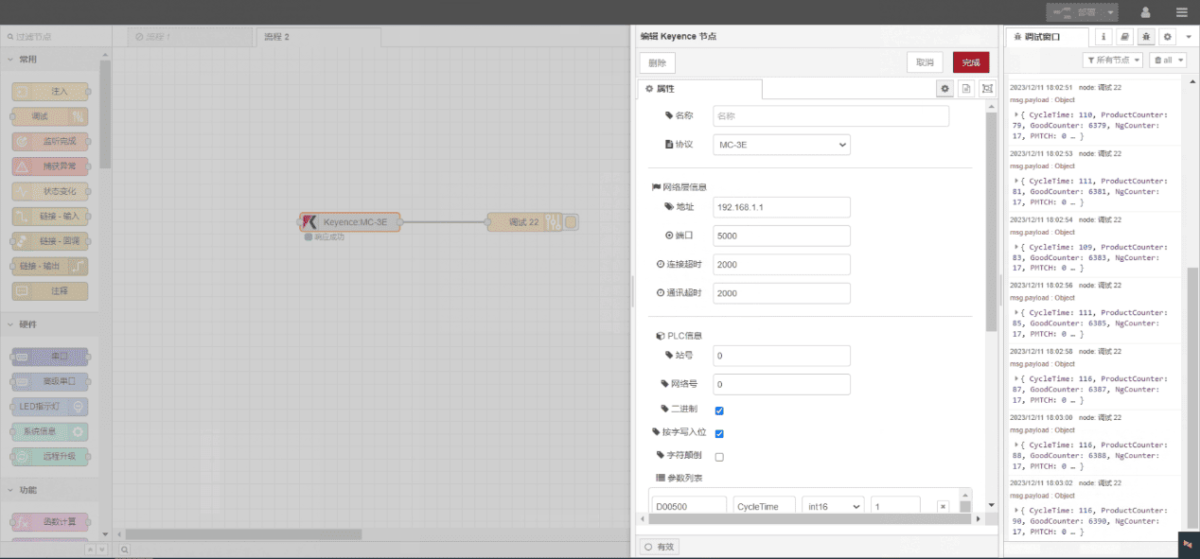
Drag a Keyence node from the left panel, double-click to open the settings page, and configure as follows based on the PLC’s communication parameters:
Protocolo: MC-3E
Network Port: Connected to the gateway’s LAN port
Endereço: 192.168.1.1
Porto: 5000
Tempo limite de ligação: 2000
Tempo limite de comunicação: 2000
ID da estação: 0
Network ID: 0
Binary: √
3.2. Configuração do ponto de dados
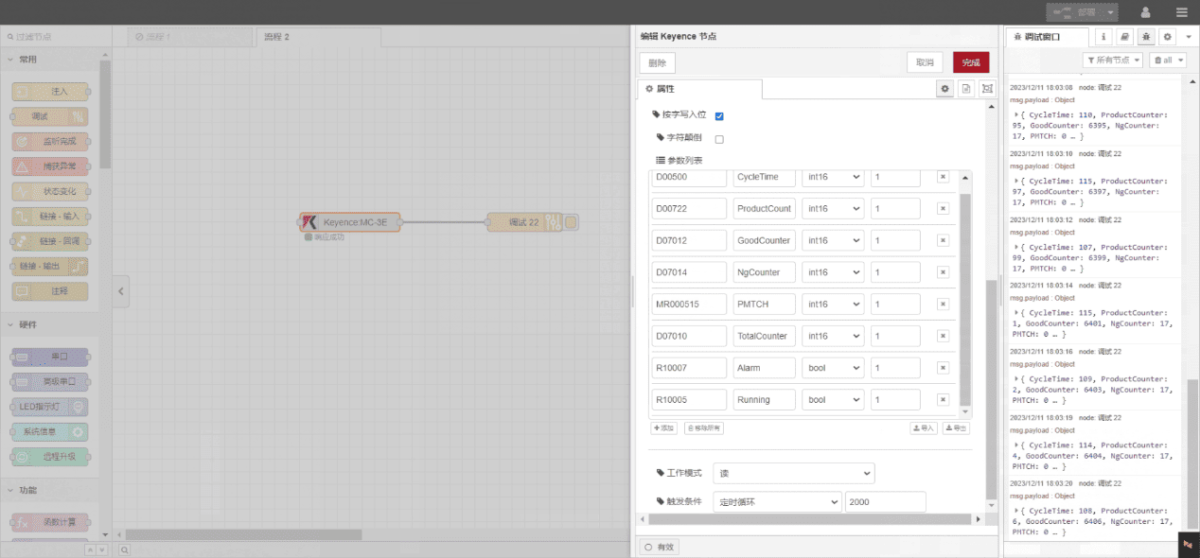
Enter the data points to be read into the parameter list of the Keyence node. Once configured, the node will automatically read data from the PLC at the specified frequency.
Data points are typically provided by PLC engineers. Upon receiving the point list, fill in the data points according to the gateway’s required format. For specific correspondence, refer to:
This is a Yueque content card. Click the link to view:(Pode utilizar o Google Chrome para traduzir) https://iotrouter.yuque.com/zn3vdn/eg8000/wgvrbfp0ivzdod3h
This example reads data from multiple addresses such as DM00500 and DM00722. In the parameter list, enter each entry in the following order: Address/Name/Data Type/Data Length. The data is read cyclically every 2 seconds, as shown in the diagram:
3.3. Ensaios
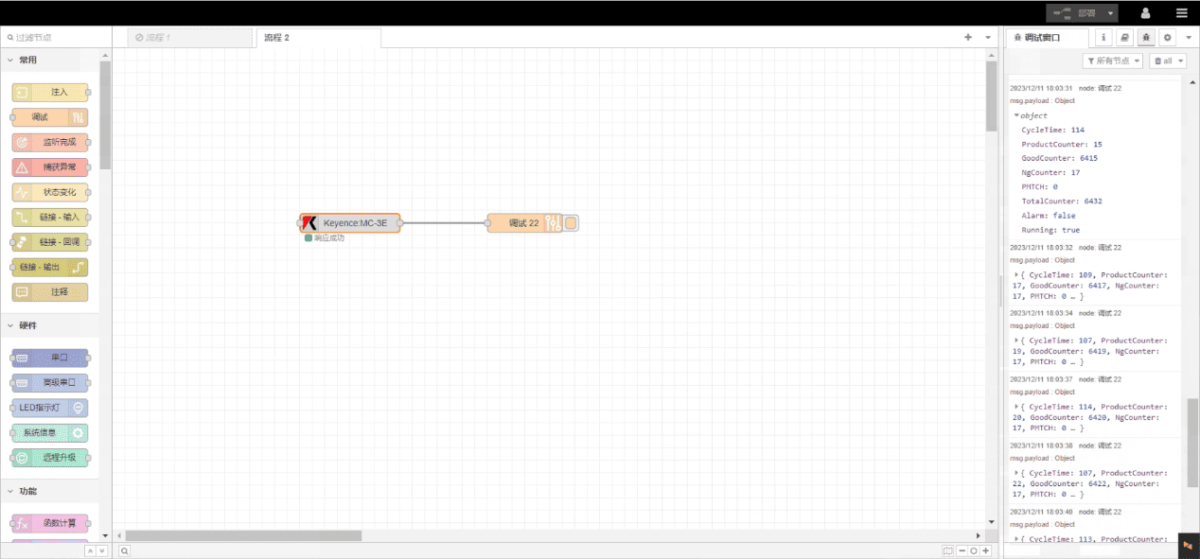
Click Deploy and observe that a data point is printed every 2 seconds. Verify that the returned data point name and corresponding value appear—communication is successful!