In recent years, with the continuous growth of data volume in industrial settings, enterprises have begun to shift their technical architecture from “single cloud deployment” to “cloud-edge-device collaboration.” Cloud computing, edge computing, endpoint computing, and fog computing form a layered system to address different computing scenarios and real-time requirements. Although these four are often mentioned together, they differ significantly in their roles, capabilities, and applicable scenarios.
I. Starting with the Cloud
Cloud computing was the first to gain popularity. The cloud is essentially a massive computing center; you send your data there, and they do the calculations for you. It boasts advantages such as low cost, high computing power (hundreds or thousands of servers in vendor data centers), and rapid scalability.
The shortcomings of cloud computing: Industrial sites are experiencing increasingly large volumes of equipment data, requiring real-time decision-making, such as robots, unmanned vehicles, and fan vibration analysis that need to make judgments within 20ms. If all data has to “run to the cloud and back,” the latency is too high, and uncontrollable factors such as network jitter and packet loss can easily occur.
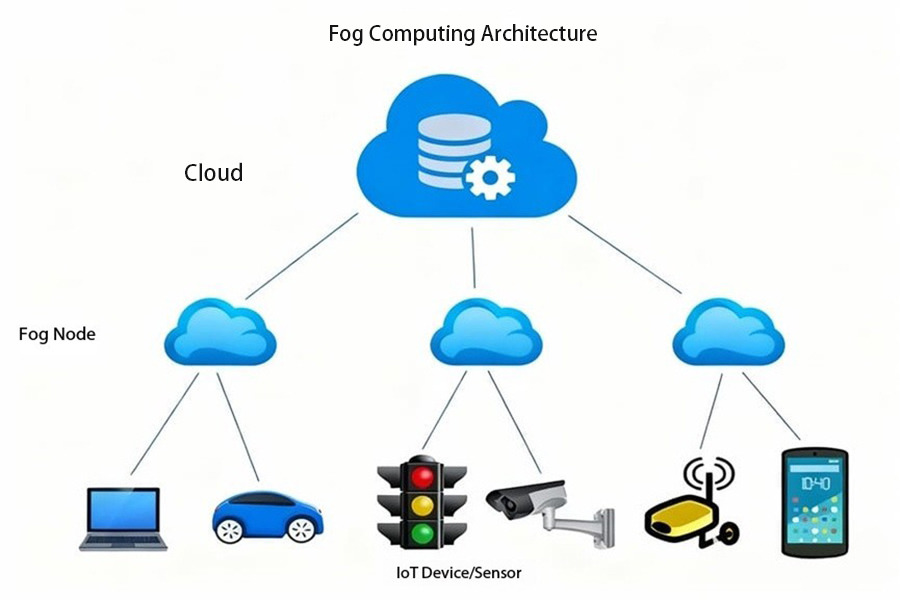
II. Fog Computing: The “Mid-Level Brain”
If the cloud is at the top and the edge is at the bottom, then fog computing is like “the cloud slowly sinking to the ground to form a fog layer.” It’s more like a distributed computing network, not placing computing power on a single device, but rather on multiple nodes across an entire region—for example, a fog layer composed of multiple base stations and roadside units in a city.
Fog computing primarily solves: regional-level data collaboration (e.g., collaborative processing of multiple subsystems in a smart park), task allocation and scheduling between edge nodes, and load balancing among multiple edge devices.
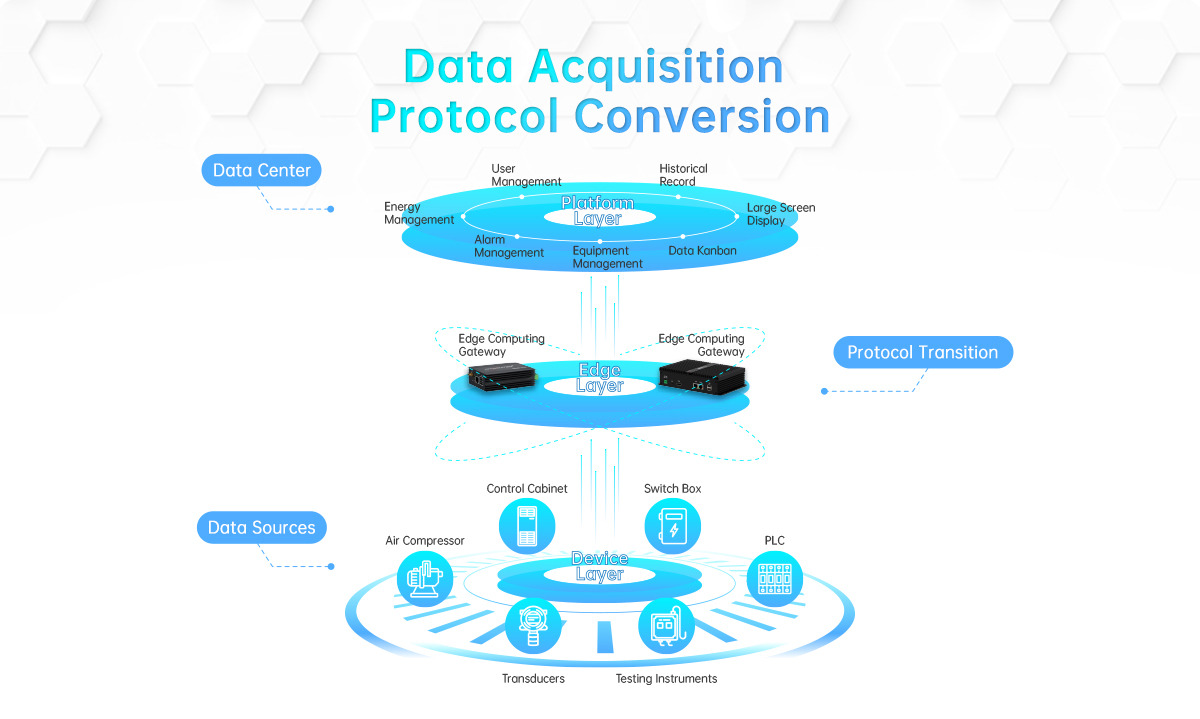
III. Edge Computing: On-Site Data Acquisition
The essence of граничные вычисления is to “move” some computing power from the cloud to locations closer to the data source, such as next to a factory production line, under an outdoor base station, or inside a server rack. In other words, anything that can be computed locally doesn’t need to go to the cloud.
Edge computing solves several key pain points:
Низкая задержка: Data is processed locally, without traveling long distances over the network.
More Reliable: Even with a network outage, local business operations can continue.
More Secure: Sensitive data doesn’t necessarily need to be uploaded to the cloud.
…
This is why edge computing has become so popular in recent years, especially in the industrial, energy, power, and transportation sectors. For example, Интеллектуальное управление Zongheng is one of the companies deeply involved in edge computing industrial gateways. Its mainstream EG edge computing gateway series can collect data from PLCs, sensors, and cameras on-site and perform real-time protocol parsing, model inference, and edge alarm processing, making it a typical “edge computing deployment device.” Below, we will specifically introduce its application value.
IV. On-device Computing: Closer to the Data
On-device/End Computing is the layer closest to the data source. It is not a gateway or a server room, but rather: the MCU/IPC inside a robot, the AI chip in a camera, the microprocessor in a smart sensor, etc. They can perform lightweight computing themselves, such as edge AI recognition, simple policy judgment, and roughly filtering data before uploading.
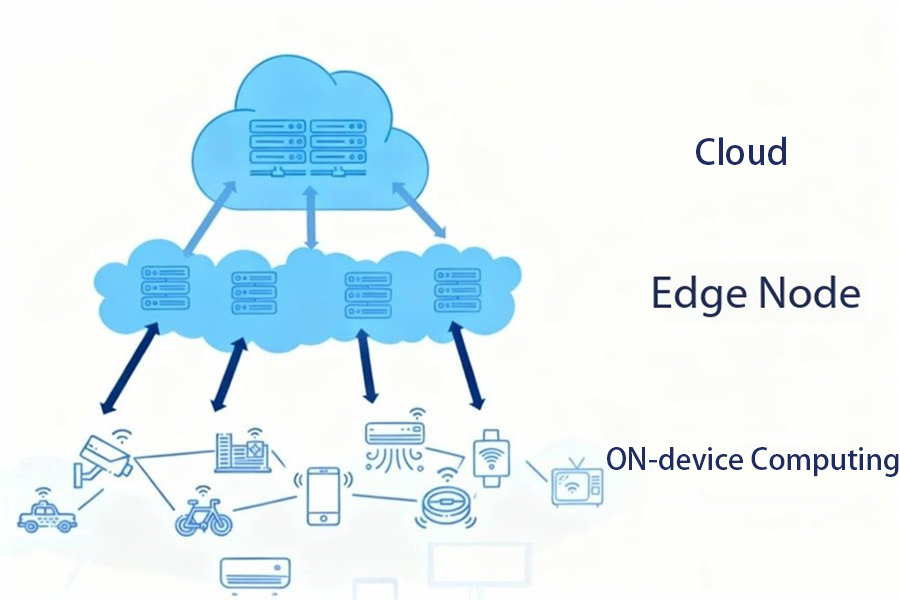
In short: Edge computing is the smallest unit of computing power locally. Many AIoT devices are now evolving towards “edge-side intelligence,” such as cameras directly performing target recognition instead of pushing all video to a server.
V. Why Does Edge Computing Need More in Industrial Scenarios?
In short: Data is too large, latency is too sensitive, and the cloud is too far away.
In traditional industrial settings, the past practice was to upload all data to the cloud. However, modern equipment is becoming increasingly intelligent, generating ever-increasing amounts of data: a single production line can generate tens of gigabytes of equipment data per day; a factory may have hundreds of PLCs, robots, servo drives, and cameras producing 30 frames per second of high-definition video, with even more demanding computing requirements. Uploading all this data to the cloud?
It’s impractical, insecure, and the latency is unbearable. Therefore, edge computing becomes the optimal solution: data is processed locally first, important results are then uploaded to the cloud, and the cloud performs long-term analysis and model training.
VI. How exactly is edge computing implemented in the field?
Taking the Интеллектуальное управление Zongheng high-performance industrial edge gateway EG8200Pro as an example, its features include:
1. AI Empowerment: Built-in independent NPU supports lightweight AI application development (such as edge detection and facial recognition).
2. Multi-Network Communication: Supports redundant access to multiple networks including 5G (optional), 4G, Ethernet, and WiFi, with self-recovery after network outages.
3. Abundant Interfaces: Equipped with 3 RS485 ports, 1 RS232 port, 2DO+2DI+2AO+2AI ports, HDMI, USB, etc.
4. Protocol Compatibility: Compatible with 30+ brand PLC protocols (such as Siemens, Mitsubishi, Omron), supporting Modbus, MQTT, HTTP, etc.
5. Data Acquisition: Millisecond-level acquisition, unlimited data points, supports network interruption resumption and data retransmission.
6. Programming Development: Visual drag-and-drop programming and JavaScript secondary development, allowing for customized data processing logic.
7. Remote Functionality: Supports remote VLANs, remote upload/download, remote configuration, and diagnostics.
8. Industrial-Grade Design: Wide temperature range of -40℃ to +85℃, surge protection, optocoupler isolation, ISO9001/14001/45001 and CE/FCC certified.
9. Web Configuration: Free web configuration tool, direct HDMI output, quickly build a data visualization interface.
10. GPS Positioning: Supports high-precision GPS satellite positioning, suitable for outdoor applications.
User Documentation:https://iotrouter.yuque.com/zn3vdn/eg8000

Zongheng Intelligent Control’s edge computing gateway series plays the role of a core node in the “end-edge-cloud” collaboration. They do not simply report data, but rather build a capability system based on the real needs of industrial sites.
Zongheng Intelligent Control’s edge computing gateways act as core data nodes in the field, achieving unified data collection from heterogeneous devices through compatibility with multiple industrial protocols (such as S7, Mitsubishi, and Modbus). They convert underlying registers into structured engineering quantities, reducing on-site adaptation work. Preprocessing such as filtering, aggregation, and threshold judgment can be completed locally before writing to Zongheng Cloud or third-party platforms, effectively reducing cloud load. The gateway has a built-in web configuration, allowing direct viewing of trends and status, maintaining basic monitoring capabilities even when the cloud is unavailable.
Simultaneously,the device supports Node-RED drag-and-drop programming, facilitating rapid construction of data collection processes and edge logic without complex coding. With cloud-edge collaboration via MQTT/HTTP/OPC UA and other methods, coupled with multi-network and industrial-grade reliability design (wide temperature range, interference resistance, etc.), the gateway can perform real-time processing locally, while the cloud handles long-term analysis and model management, forming a complete edge intelligence system.
Finally
cloud-fog-edge-device—this is not just a technological shift, but a “computing power migration” of the entire digital world. Future intelligent manufacturing, intelligent power, and smart cities all rely on a collaborative system of edge-fog-cloud. Edge computing is becoming a core key. It is both the closest “rapid response” layer to the field and the foundation for industry intelligence.
If you are planning factory digitization, equipment networking, or edge intelligence, consider Zongheng Intelligent Control’s edge computing gateway—grounded in the field, stable and reliable, it’s a tool that can be directly implemented in real-world industries.